Effects of Bacillus subtilis T6-1 on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure of Continuous Cropping Poplar
- PMID: 35625519
- PMCID: PMC9138279
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11050791
Effects of Bacillus subtilis T6-1 on the Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structure of Continuous Cropping Poplar
Abstract
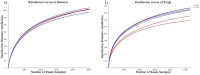
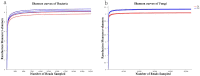
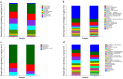
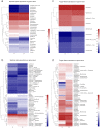
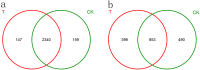
The continuous cropping obstacles in poplar cultivation cause declines in wood yield and serious soil-borne diseases, mainly because of structural alterations in the microbial community and the aggregation of pathogenic fungi. Bacillus subtilis T6-1, isolated from poplar rhizospheric soil, has strong antagonistic effects on poplar pathogens. We aimed to investigate the effects of B. subtilis T6-1 on the structure of the microbial community in the poplar rhizosphere. Poplar seedlings were replanted in three successive generations of soil. The diameter at breast height, plant height, and the number of culturable bacteria of the poplars inoculated with T6-1 exceeded those in the non-inoculated control group. qPCR analysis revealed that the total abundance of T6-1 bacteria in the treated poplars was remarkably higher in contrast to that in the control group. Illumina MiSeq sequencing was employed to track the alterations in diversity and structure of the total microbial community in the poplar rhizosphere inoculated with B. subtilis T6-1. Fungal diversity and abundance in the T6-1 rhizosphere were remarkably lower in contrast with those in the control rhizosphere. The proportion of Bacillus sp. in the total bacterial community in the T6-1 and control groups was 3.04% and 2.38%, respectively, while those of the Rhizoctonia sp. was 2.02% and 5.82%, respectively. In conclusion, B. subtilis T6-1 has the potential to serve as a microbial agent, enhancing the structure of the rhizosphere microbial community as well as promoting tree growth in poplar cultivation.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis; continuous cropping obstacles; microbiology community structure; poplar; rhizosphere.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Xi B., Clothier B., Coleman M., Duan J., Hu W., Li D., Di N., Liu Y., Fu J., Li J., et al. Irrigation management in poplar (Populus spp.) plantations: A review. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021;494:119330. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119330. - DOI
-
- Wang Y., Bai G., Shao G., Cao Y. An analysis of potential investment returns and their determinants of poplar plantations in state-owned forest enterprises of China. New For. 2014;45:251–264. doi: 10.1007/s11056-014-9406-z. - DOI
-
- Cheng S., Xu Z., Su Y., Zhen L. Spatial and temporal flows of China’s forest resources: Development of a framework for evaluating resource efficiency. Ecol. Econ. 2010;69:1405–1415. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.04.006. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

