Presence of Protease Inhibitor 9 and Granzyme B in Healthy and Pathological Human Corneas
- PMID: 35625521
- PMCID: PMC9138262
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11050793
Presence of Protease Inhibitor 9 and Granzyme B in Healthy and Pathological Human Corneas
Abstract
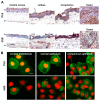
The aim of this study was to find out whether protease inhibitor 9 (PI-9) and granzyme B (GrB) molecules that contribute to immune response and the immunological privilege of various tissues are expressed in healthy and pathological human corneas. Using cryosections, cell imprints of control corneoscleral discs, we showed that PI-9 was expressed particularly in the endothelium, the superficial and suprabasal epithelium of healthy corneas, limbus, and conjunctiva. GrB was localized in healthy corneal and conjunctival epithelium, while the endothelium showed weak immunostaining. The expression of PI-6 and GrB was confirmed by qRT-PCR. Increased expression levels of the PI-9 and GrB genes were determined when the corneas were cultured with proinflammatory cytokines. Fluorescent and enzymatic immunohistochemistry of pathological corneal explants (corneal melting and herpes virus keratitis) showed pronounced PI-9, GrB, human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DR, and leukocyte-common antigen (CD45) signals localized in multicellular stromal infiltrates and inflammatory cells scattered in the corneal stroma. We conclude that increased expression of the PI-9 and GrB proteins under pathological conditions and their upregulation in an inflammatory environment indicate their participation in immune response of the cornea during the inflammatory process.
Keywords: cornea; corneal endothelium; corneal epithelium; granzyme B; protease inhibitor 9.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bird C.H., Blink E.J., Hirst C.E., Buzza M.S., Steele P.M., Sun J., Jans D.A., Bird P.I. Nucleocytoplasmic distribution of the ovalbumin serpin PI-9 requires a nonconventional nuclear import pathway and the export factor Crm1. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;21:5396–5407. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.16.5396-5407.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sun J., Bird C.H., Sutton V., McDonald L., Coughlin P.B., De Jong T.A., Trapani J.A., Bird P.I. A cytosolic granzyme B inhibitor related to the viral apoptotic regulator cytokine response modifier A is present in cytotoxic lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:27802–27809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27802. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- MSMT-28477/2014,7F14156/Norwegian Financial Mechanism 2009-2014 and the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic
- BBMRI_CZ LM 2018125/Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic
- 001/Charles University, Prague, Cooperatio: Medical Diagnostics and Basic Medical Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

