Comparative Analysis of rRNA Removal Methods for RNA-Seq Differential Expression in Halophilic Archaea
- PMID: 35625610
- PMCID: PMC9138242
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12050682
Comparative Analysis of rRNA Removal Methods for RNA-Seq Differential Expression in Halophilic Archaea
Abstract
Despite intense recent research interest in archaea, the scientific community has experienced a bottleneck in the study of genome-scale gene expression experiments by RNA-seq due to the lack of commercial and specifically designed rRNA depletion kits. The high rRNA:mRNA ratio (80-90%: ~10%) in prokaryotes hampers global transcriptomic analysis. Insufficient ribodepletion results in low sequence coverage of mRNA, and therefore, requires a substantially higher number of replicate samples and/or sequencing reads to achieve statistically reliable conclusions regarding the significance of differential gene expression between case and control samples. Here, we show that after the discontinuation of the previous version of RiboZero (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) that was useful in partially or completely depleting rRNA from archaea, archaeal transcriptomics studies have experienced a slowdown. To overcome this limitation, here, we analyze the efficiency for four different hybridization-based kits from three different commercial suppliers, each with two sets of sequence-specific probes to remove rRNA from four different species of halophilic archaea. We conclude that the key for transcriptomic success with the currently available tools is the probe-specificity for the rRNA sequence hybridization. With this paper, we provide insights into the archaeal community for selecting certain reagents and strategies over others depending on the archaeal species of interest. These methods yield improved RNA-seq sensitivity and enhanced detection of low abundance transcripts.
Keywords: RNAs-seq; archaea; halophiles; rRNA removal; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

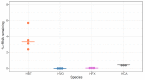

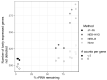
Similar articles
-
Comparison of rRNA depletion methods for efficient bacterial mRNA sequencing.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 6;12(1):5765. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09710-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35388078 Free PMC article.
-
A Simple, Cost-Effective, and Robust Method for rRNA Depletion in RNA-Sequencing Studies.mBio. 2020 Apr 21;11(2):e00010-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00010-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32317317 Free PMC article.
-
Improved bacterial RNA-seq by Cas9-based depletion of ribosomal RNA reads.RNA. 2020 Aug;26(8):1069-1078. doi: 10.1261/rna.075945.120. Epub 2020 Apr 28. RNA. 2020. PMID: 32345633 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleoproteins in archaeal pre-rRNA processing and modification.Archaea. 2013;2013:614735. doi: 10.1155/2013/614735. Epub 2013 Mar 10. Archaea. 2013. PMID: 23554567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small regulatory RNAs in Archaea.RNA Biol. 2014;11(5):484-93. doi: 10.4161/rna.28452. Epub 2014 Mar 31. RNA Biol. 2014. PMID: 24755959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A single workflow for multi-species blood transcriptomics.BMC Genomics. 2024 Mar 16;25(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10208-2. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38493105 Free PMC article.
-
Haloferax volcanii: a versatile model for studying archaeal biology.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jun 24;207(6):e0006225. doi: 10.1128/jb.00062-25. Epub 2025 May 14. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40366157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive guide for epigenetics and transcriptomics data quality control.STAR Protoc. 2025 Mar 21;6(1):103607. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2025.103607. Epub 2025 Jan 26. STAR Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39869481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A sweet new set of inducible and constitutive promoters in Haloferax volcanii.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 10;14:1204876. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1204876. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37637112 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin landscape of the euryarchaeon Haloferax volcanii.Genome Biol. 2023 Nov 6;24(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03095-5. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37932847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bainbridge M.N., Warren R.L., Hirst M., Romanuik T., Zeng T., Go A., Delaney A., Griffith M., Hickenbotham M., Magrini V., et al. Analysis of the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP transcriptome using a sequencing-by-synthesis approach. BMC Genom. 2006;7:246. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-246. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

