Cathelicidin LL-37 in Health and Diseases of the Oral Cavity
- PMID: 35625823
- PMCID: PMC9138798
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10051086
Cathelicidin LL-37 in Health and Diseases of the Oral Cavity
Abstract
The mechanisms for maintaining oral cavity homeostasis are subject to the constant influence of many environmental factors, including various chemicals and microorganisms. Most of them act directly on the oral mucosa, which is the mechanical and immune barrier of the oral cavity, and such interaction might lead to the development of various oral pathologies and systemic diseases. Two important players in maintaining oral health or developing oral pathology are the oral microbiota and various immune molecules that are involved in controlling its quantitative and qualitative composition. The LL-37 peptide is an important molecule that upon release from human cathelicidin (hCAP-18) can directly perform antimicrobial action after insertion into surface structures of microorganisms and immunomodulatory function as an agonist of different cell membrane receptors. Oral LL-37 expression is an important factor in oral homeostasis that maintains the physiological microbiota but is also involved in the development of oral dysbiosis, infectious diseases (including viral, bacterial, and fungal infections), autoimmune diseases, and oral carcinomas. This peptide has also been proposed as a marker of inflammation severity and treatment outcome.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptides; human cathelicidin; immunomodulation; oral cavity.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
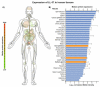


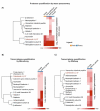


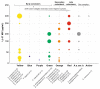



 , i.e., up- or downregulation) and their correlation with the periodontal status (
, i.e., up- or downregulation) and their correlation with the periodontal status ( , represented by probing depth, PD; bleeding on probing, BOP; clinical attachment loss, CAL; plaque index, PI; gingival index, GI; papillary bleeding index, PBI) and microbiological parameters (
, represented by probing depth, PD; bleeding on probing, BOP; clinical attachment loss, CAL; plaque index, PI; gingival index, GI; papillary bleeding index, PBI) and microbiological parameters ( , i.e., changes in occurrence of P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, and T. denticola) were obtained from the references [5,6,113].
, i.e., changes in occurrence of P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, and T. denticola) were obtained from the references [5,6,113].

Similar articles
-
The human cathelicidin hCAP18/LL-37: a multifunctional peptide involved in mycobacterial infections.Peptides. 2010 Sep;31(9):1791-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.06.016. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 20600427 Review.
-
The human cathelicidin LL-37--A pore-forming antibacterial peptide and host-cell modulator.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Mar;1858(3):546-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26556394 Review.
-
Antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin LL-37 preserves intestinal barrier and organ function in rats with heat stroke.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 May;161:114565. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114565. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36958193
-
The host defence peptide LL-37/hCAP-18 is a growth factor for lung cancer cells.Lung Cancer. 2008 Jan;59(1):12-23. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2007.07.014. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Lung Cancer. 2008. PMID: 17764778
-
The Role of Cathelicidin LL-37 in Cancer Development.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016 Feb;64(1):33-46. doi: 10.1007/s00005-015-0359-5. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016. PMID: 26395996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Significance of host antimicrobial peptides in the pathogenesis and treatment of acne vulgaris.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 18;15:1502242. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1502242. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39744637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Epigenetic Modifications on Different Facets in the Periodontal Pathogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 30;14(6):1202. doi: 10.3390/genes14061202. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Synthetic Analogues for Effective Oral Microflora Control and Oral Infection Treatment-The Role of Ceragenins in the Development of New Therapeutic Methods.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;17(12):1725. doi: 10.3390/ph17121725. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial periodontal ligament stem cells enhance periodontal regeneration and regulate the oral microbiome.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):334. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03939-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39334342 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm properties of cathelicidin LL-37: an in-depth review.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 14;39(4):99. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03545-z. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36781570 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

