Gasdermin D Deficiency Limits the Transition of Atherosclerotic Plaques to an Inflammatory Phenotype in ApoE Knock-Out Mice
- PMID: 35625908
- PMCID: PMC9138554
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10051171
Gasdermin D Deficiency Limits the Transition of Atherosclerotic Plaques to an Inflammatory Phenotype in ApoE Knock-Out Mice
Abstract
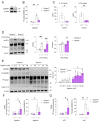
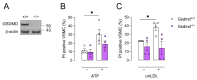
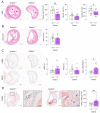
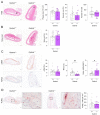
Gasdermin D (GSDMD) is the key executor of pyroptotic cell death. Recent studies suggest that GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis is involved in atherosclerotic plaque destabilization. We report that cleaved GSDMD is expressed in macrophage- and smooth muscle cell-rich areas of human plaques. To determine the effects of GSDMD deficiency on atherogenesis, ApoE-/- Gsdmd-/- (n = 16) and ApoE-/-Gsdmd+/+ (n = 18) mice were fed a western-type diet for 16 weeks. Plaque initiation and formation of stable proximal aortic plaques were not altered. However, plaques in the brachiocephalic artery (representing more advanced lesions compared to aortic plaques) of ApoE-/- Gsdmd-/- mice were significantly smaller (115 ± 18 vs. 186 ± 16 × 103 µm2, p = 0.006) and showed features of increased stability, such as decreased necrotic core area (19 ± 4 vs. 37 ± 7 × 103 µm2, p = 0.03) and increased αSMA/MAC3 ratio (1.6 ± 0.3 vs. 0.7 ± 0.1, p = 0.01), which was also observed in proximal aortic plaques. Interestingly, a significant increase in TUNEL positive cells was observed in brachiocephalic artery plaques from ApoE-/- Gsdmd-/- mice (141 ± 25 vs. 62 ± 8 cells/mm2, p = 0.005), indicating a switch to apoptosis. This switch from pyroptosis to apoptosis was also observed in vitro in Gsdmd-/- macrophages. In conclusion, targeting GSDMD appears to be a promising approach for limiting the transition to an inflammatory, vulnerable plaque phenotype.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; gasdermin D; inflammation; pyroptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

