Metastasis-Directed Radiation Therapy with Consolidative Intent for Oligometastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35625979
- PMCID: PMC9139743
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14102373
Metastasis-Directed Radiation Therapy with Consolidative Intent for Oligometastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
The management of patients with oligometastatic urothelial carcinoma (UC) represents an evolving field in uro-oncology, and the role of metastasis-directed therapies, including metastasectomy and metastasis-directed radiation therapy (MDRT), is gaining increasing attention. Herein, we summarize available evidence about the role of MDRT with consolidative intent in oligometastatic UC patients. A systematic review was performed in December 2021. Six studies involving 158 patients were identified. Most patients (n = 120, 90.2%) had a history of bladder cancer and the most frequent sites of metastases were lymph nodes (n = 61, 52.1%) followed by the lungs (n = 34, 29%). Overall, 144 metastases were treated with MDRT. Median follow-up ranged from 17.2 to 25 months. Local control rates ranged from 57% to 100%. Median Overall Survival (OS) ranged from 14.9 to 51.0 months and median progression-free survival ranged from 2.9 to 10.1 months. Rates of OS at one and two years ranged from 78.9% to 96% and from 26% to 63%, respectively. Treatment-related toxicity was recorded in few patients and in most cases a low-grade toxicity was evident. MDRT with consolidative intent represents a potential treatment option for selected patients with oligometastatic UC.
Keywords: bladder cancer; oligometastatic disease; radiotherapy; upper urinary transitional cell carcinoma; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
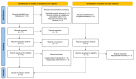



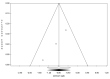
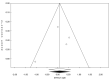
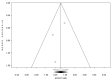
References
-
- Witjes J.A., Bruins H.M., Cathomas R., Compérat E.M., Cowan N.C., Gakis G., Hernández V., Linares Espinós E., Lorch A., Neuzillet Y., et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2020 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021;79:82–104. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.03.055. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tarantino G., Crocetto F., Di Vito C., Creta M., Martino R., Pandolfo S.D., Pesce S., Napolitano L., Capone D., Imbimbo C. Association of NAFLD and Insulin Resistance with Non Metastatic Bladder Cancer Patients: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021;10:346. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020346. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Collà Ruvolo C., Nocera L., Stolzenbach L.F., Wenzel M., Califano G., Tian Z., Verze P., Shariat S.F., Saad F., Briganti A., et al. Tumor Size Predicts Muscle-invasive and non-organ-confined Disease in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma at Radical Nephroureterectomy. Eur. Urol. Focus. :2021. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.03.003. in press. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

