The Genetic Architecture of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Hungary: Analysis of 242 Patients with a Panel of 98 Genes
- PMID: 35626289
- PMCID: PMC9139509
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12051132
The Genetic Architecture of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Hungary: Analysis of 242 Patients with a Panel of 98 Genes
Abstract
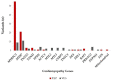
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium most commonly caused by mutations in sarcomeric genes. We aimed to perform a nationwide large-scale genetic analysis of a previously unreported, representative HCM cohort in Hungary. A total of 242 consecutive HCM index patients (127 men, 44 ± 11 years) were studied with next generation sequencing using a custom-designed gene-panel comprising 98 cardiomyopathy-related genes. A total of 90 patients (37%) carried pathogenic/likely pathogenic (P/LP) variants. The percentage of patients with P/LP variants in genes with definitive evidence for HCM association was 93%. Most of the patients with P/LP variants had mutations in MYBPC3 (55 pts, 61%) and in MYH7 (21 pts, 23%). Double P/LP variants were present in four patients (1.7%). P/LP variants in other genes could be detected in ≤3% of patients. Of the patients without P/LP variants, 46 patients (19%) carried a variant of unknown significance. Non-HCM P/LP variants were identified in six patients (2.5%), with two in RAF1 (p.Leu633Val, p.Ser257Leu) and one in DES (p.Arg406Trp), FHL1 (p.Glu96Ter), TTN (p.Lys23480fs), and in the mitochondrial genome (m.3243A>G). Frameshift, nonsense, and splice-variants made up 82% of all P/LP MYBPC3 variants. In all the other genes, missense mutations were the dominant form of variants. The MYBPC3 p.Gln1233Ter, the MYBPC3 p.Pro955ArgfsTer95, and the MYBPC3 p.Ser593ProfsTer11 variants were identified in 12, 7, and 13 patients, respectively. These three variants made up 36% of all patients with identified P/LP variants, raising the possibility of a possible founder effect for these mutations. Similar to other HCM populations, the MYBPC3 and the MYH7 genes seemed to be the most frequently affected genes in Hungarian HCM patients. The high prevalence of three MYBPC3 mutations raises the possibility of a founder effect in our HCM cohort.
Keywords: genetic analysis; genetic variant; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Elliott P.M., Anastasakis A., Borger M.A., Borggrefe M., Cecchi F., Charron P., Hagege A.A., Lafont A., Limongelli G., Mahrholdt H., et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on diagnosis and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur. Heart J. 2014;35:2733–2779. - PubMed
-
- Maron B.J., Gardin J.M., Flack J.M., Gidding S.S., Kurosaki T.T., Bild D.E. Prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a general population of young adults. Echocardiographic analysis of 4111 subjects in the CARDIA Study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in (Young) Adults. Circulation. 1995;92:785–789. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.92.4.785. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonne G., Carrier L., Bercovici J., Cruaud C., Richard P., Hainque B., Gautel M., Labeit S., James M., Beckmann J., et al. Cardiac myosin binding protein-C gene splice acceptor site mutation is associated with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat. Genet. 1995;11:438–440. doi: 10.1038/ng1295-438. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous