Rapid Quantum Magnetic IL-6 Point-of-Care Assay in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19
- PMID: 35626318
- PMCID: PMC9139897
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12051164
Rapid Quantum Magnetic IL-6 Point-of-Care Assay in Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19
Abstract
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has been linked to several life-threatening disease processes. Developing a point-of-care testing platform for the immediate and accurate detection of IL-6 concentrations could present a valuable tool for improving clinical management in patients with IL-6-mediated diseases. Drawing on an available biobank of samples from 35 patients hospitalized with COVID-19, a novel quantum-magnetic sensing platform is used to determine plasma IL-6 concentrations. A strong correlation was observed between IL-6 levels measured by QDTI10x and the Luminex assay (r = 0.70, p-value < 0.001) and between QDTI80x and Luminex (r = 0.82, p-value < 0.001). To validate the non-inferiority of QDTI to Luminex in terms of the accuracy of IL-6 measurement, two clinical parameters—the need for intensive care unit admission and the need for mechanical intubation—were chosen. IL-6 concentrations measured by the two assays were compared with respect to these clinical outcomes. Results demonstrated a comparative predictive performance between the two assays with a significant correlation coefficient. Conclusion: In short, the QDTI assay holds promise for implementation as a potential tool for rapid clinical decision in patients with IL-6-mediated diseases. It could also reduce healthcare costs and enable the development of future various biomolecule point-of-care tests for different clinical scenarios.
Keywords: COVID-19; ICU; IL-6; Luminex; QDTI; diagnostics; mechanical ventilation.
Conflict of interest statement
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
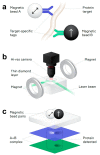
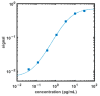

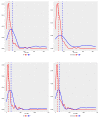

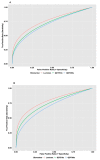
References
-
- Dinnes J., Deeks J.J., Berhane S., Taylor M., Adriano A., Davenport C., Dittrich S., Emperador D., Takwoingi Y., Cunningham J., et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021;2021:CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.cd013705.pub2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rawling D., Nie W., Remmel M., Eshoo M., Romanowsky J., Liesenfeld O., Sweeney T. 2021. An Ultra-Rapid Host Response Assay to Discriminate Between Bacterial and Viral Infections Using Quantitative Isothermal Gene Expression Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018;5((Suppl. 1)):S589. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy210.1677. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

