Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Our Experience Based on 35-Years Follow-Up
- PMID: 35626329
- PMCID: PMC9139921
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12051174
Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Our Experience Based on 35-Years Follow-Up
Abstract
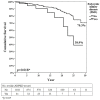
Background and objectives: For patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), the best replacement therapy is renal transplant (RTx) to ensure life with good quality. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a genetic disorder and a common cause of ESRD. Different from ESRD of other causes, ADPKD patients need careful pre-RTx evaluations like detecting the presence of intracranial aneurisms, cardiac manifestations, and complications of liver and renal cysts. Materials: We retrieved a total of 1327 RTx patients receiving 1382 times RTx (two recipients with three times, 48 recipients with two times) over the last 35 years. Only 41 of these patients were diagnosed with ADPKD. Results: At the first RTx, patients’ ages were 42.9 ± 12.6 (mean ± SD) years. Ages of the ADPKD group (52.5 ± 10.1 years) were older than the non-ADPKD group (42.7 ± 12.7 years, p = 0.001). We found more cell mediated and antibody mediated rejection (29.3% vs. 26.0%, and 22.0% vs. 7.0%; both p < 0.001), new onset diabetes after transplant (NODAT) (21, 51.2% vs. 326, 25.3%; p = 0.005), and worse graft survival (p < 0.001) in the ADPKD group, and with the development of more malignancies (18; 43.9% vs. 360; 28.0%; p = 0.041). The long-term patient survivals were poorer in the ADPKD group (38.9% vs. 70.3%; p = 0.018). ADPKD was found as an independent risk factor for long-term patient survival (HR = 2.64, 95% CI 1.03−6.76, p = 0.04). Conclusions: Patients with ADPKD-related ESRD developed more NODAT, and also more malignancies if not aggressively surveyed before surgery. Due to poor long-term graft and patient survivals, regular careful examinations for NODAT and malignancies, even in the absence of related symptoms and signs, are highly recommended in the follow-ups.
Keywords: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; malignancy; new onset diabetes mellitus after transplantation; patient survival; renal transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roozbeh J., Razmkon A.R., Jalaeian H., Raiss-Jalali G.A., Behzadi S., Sagheb M.M., Salahi H., Bahador A., Nikeghbalian S., Davari H.R., et al. Outcome of kidney transplantation in patients with polycystic kidney disease: A single center study. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 2008;19:72–75. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources