Central Nervous System Pericytes Contribute to Health and Disease
- PMID: 35626743
- PMCID: PMC9139243
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11101707
Central Nervous System Pericytes Contribute to Health and Disease
Abstract
Successful neuroprotection is only possible with contemporary microvascular protection. The prevention of disease-induced vascular modifications that accelerate brain damage remains largely elusive. An improved understanding of pericyte (PC) signalling could provide important insight into the function of the neurovascular unit (NVU), and into the injury-provoked responses that modify cell-cell interactions and crosstalk. Due to sharing the same basement membrane with endothelial cells, PCs have a crucial role in the control of endothelial, astrocyte, and oligodendrocyte precursor functions and hence blood-brain barrier stability. Both cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases impair oxygen delivery and functionally impair the NVU. In this review, the role of PCs in central nervous system health and disease is discussed, considering their origin, multipotency, functions and also dysfunction, focusing on new possible avenues to modulate neuroprotection. Dysfunctional PC signalling could also be considered as a potential biomarker of NVU pathology, allowing us to individualize therapeutic interventions, monitor responses, or predict outcomes.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; angiogenesis; mesoangioblast; multiple sclerosis; neuroCOVID-19; neurodevelopmental disorders; neuroinflammation; neurovascular unit; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
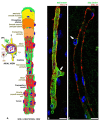

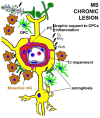
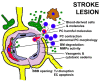
References
-
- Campagnolo P., Cesselli D., Al Haj Zen A., Beltrami A.P., Krankel N., Katare R., Angelini G., Emanueli C., Madeddu P. Human adult vena saphena contains perivascular progenitor cells endowed with clonogenic and proangiogenic potential. Circulation. 2010;121:1735–1745. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.899252. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

