Disinfecting Action of Gaseous Ozone on OXA-48-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilm In Vitro
- PMID: 35627712
- PMCID: PMC9140702
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19106177
Disinfecting Action of Gaseous Ozone on OXA-48-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Biofilm In Vitro
Abstract
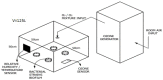
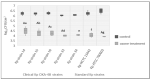
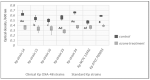
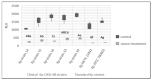
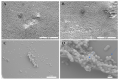
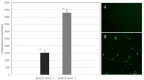
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an emerging multidrug-resistant pathogen that can contaminate hospital surfaces in the form of a biofilm which is hard to remove with standard disinfectants. Because of biofilm resistance to conservative disinfectants, the application of new disinfection technologies is becoming more frequent. Ozone gas has antimicrobial activity but there is lack of data on its action against K. pneumoniae biofilm. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects and mechanisms of action of gaseous ozone on the OXA-48-procuding K. pneumoniae biofilm. A 24 h biofilm of K. pneumoniae formed on ceramic tiles was subsequently exposed to different concentrations of ozone during one and two hours to determine the optimal ozone concentration. Afterwards, the total bacteria count, total biomass and oxidative stress levels were monitored. A total of 25 ppm of gaseous ozone was determined to be optimal ozone concentration and caused reduction in total bacteria number in all strains of K. pneumoniae for 2.0 log10 CFU/cm2, followed by reduction in total biomass up to 88.15%. Reactive oxygen species levels significantly increased after the ozone treatment at 182% for the representative K. pneumoniae NCTC 13442 strain. Ozone gas in the concentration of 25 ppm caused significant biofilm reduction but did not completely eradicate the K. pneumoniae biofilm formed on ceramics. In conclusion, ozone gas has great potential to be used as an additional hygiene measure in joint combat against biofilm in hospital environments.
Keywords: K. pneumoniae; OXA-48 disinfection; biofilm; gaseous disinfection; hospital-acquired infections; multidrug-resistant microorganisms; ozone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of different disinfection protocols against contamination of ceramic surfaces with Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024 Dec 29;75(4):289-296. doi: 10.2478/aiht-2024-75-3920. eCollection 2024 Dec 1. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024. PMID: 39718087 Free PMC article.
-
Tolerance of biofilm of a carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae involved in a duodenoscopy-associated outbreak to the disinfectant used in reprocessing.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2022 Jun 3;11(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13756-022-01112-z. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2022. PMID: 35659363 Free PMC article.
-
[Biological characteristics and genomic information of a bacteriophage against pan-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in a burn patient and its effects on bacterial biofilm].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Jan 20;36(1):14-23. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2020.01.004. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32023713 Chinese.
-
The Characteristic of Virulence, Biofilm and Antibiotic Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Aug 28;17(17):6278. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17176278. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32872324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promising strategies for future treatment of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilms.Future Microbiol. 2020 Jan;15:63-79. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2019-0180. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Future Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32048525 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of gaseous ozone treatment on cells and biofilm of dairy Bacillus spp. isolates.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 17;16:1538456. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1538456. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40165788 Free PMC article.
-
Physico-Chemical Investigation and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Ozonated Oils: The Case Study of Commercial Ozonated Olive and Sunflower Seed Refined Oils.Molecules. 2024 Feb 1;29(3):679. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030679. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338423 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of different disinfection protocols against contamination of ceramic surfaces with Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024 Dec 29;75(4):289-296. doi: 10.2478/aiht-2024-75-3920. eCollection 2024 Dec 1. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024. PMID: 39718087 Free PMC article.
-
Potent Activity of a High Concentration of Chemical Ozone against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria.Molecules. 2022 Jun 22;27(13):3998. doi: 10.3390/molecules27133998. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Passaretti C.L., Otter J.A., Reich N.G., Myers J., Shepard J., Ross T., Carroll K.C., Lipsett P., Perl T.M., Costa D.M., et al. Staphylococcus aureus dry-surface biofilms are not killed by sodium hypochlorite: Implications for infection control. Am. J. Infect. Control. 2013;44:533–542. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz092. - DOI
-
- Abram M., Škrobonja I., Ambrožić D., Repac-Antić D.B.Š.M. ESKAPE—Bacteria that alert the world. Med. Flum. 2018;54:242–253. doi: 10.21860/medflum2018_203547. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

