Dynamic Performance Assessment of Hospitals by Applying Credibility-Based Fuzzy Window Data Envelopment Analysis
- PMID: 35628013
- PMCID: PMC9141957
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10050876
Dynamic Performance Assessment of Hospitals by Applying Credibility-Based Fuzzy Window Data Envelopment Analysis
Abstract
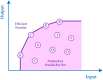
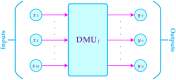
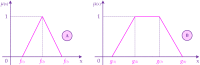
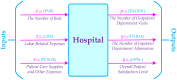
The goal of the current research is to propose the credibility-based fuzzy window data envelopment analysis (CFWDEA) approach as a novel method for the dynamic performance evaluation of hospitals during different periods under data ambiguity and linguistic variables. To reach this goal, a data envelopment analysis (DEA) method, a window analysis technique, a possibilistic programming approach, credibility theory, and chance-constrained programming (CCP) are employed. In addition, the applicability and efficacy of the proposed CFWDEA approach are illustrated utilizing a real data set to evaluate the performance of hospitals in the USA. It should be explained that three inputs including the number of beds, labor-related expenses, patient care supplies, and other expenses as well as three outputs including the number of outpatient department visits, the number of inpatient department admissions, and overall patient satisfaction level, are considered for the dynamic performance appraisal of hospitals. The experimental results show the usefulness of the CFWDEA method for the evaluation and ranking of hospitals in the presence of fuzzy data, linguistic variables, and epistemic uncertainty.
Keywords: credibility theory; data envelopment analysis; fuzzy optimization; hospital performance assessment; linguistic variables; window analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Moshiri H., Aljunid S.M., Amin R.M. Hospital efficiency: Concept, measurement techniques and review of hospital efficiency studies. Malays. J. Public Health Med. 2010;10:35–43.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

