Adaptation and Psychometric Evidence of the ARABIC Version of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (A-DSMQ)
- PMID: 35628088
- PMCID: PMC9140770
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10050951
Adaptation and Psychometric Evidence of the ARABIC Version of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (A-DSMQ)
Abstract
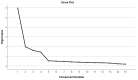
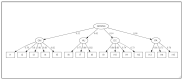
(1) Background: Diabetic patients must engage in self-care practices in order to maintain optimal glycemic control, hence reducing the likelihood of developing complications, and enhance the overall quality of their lives. The Diabetes Self-care Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) is a tool for assessing self-management habits that may be used to predict glycemic control in people with diabetes. However, no Arabic language version of the instrument has been found. Therefore, we adapted an Arabic language version of the instrument in Tunisia. The purpose of the current research aimed to assess the psychometric features of the Tunisian version of the DSMQ in patients with type 2 diabetes. (2) Method: Two samples including both genders, one exploratory (n = 208, mean age 53.2 ± 8.3) and one confirmatory (n = 441, mean age 53.4 ± 7.4), completed an adapted Arabic language version of the DSMQ, a sociodemographic questionnaire and information about their HbA1C levels. (3) Results: The exploratory factor analysis revealed that the 15 items of the A-DSMQ fit well with the data. Likewise, the alpha coefficients for the A-DSMQ factors were above 0.80: for "Glucose Management" (GM), "Dietary Control" (DC), "Physical Activity" (PA), and "Heath-Care Use" (HU). The fit indices for the CFA were good, and the four-factor solution was confirmed. The Average Variance Extracted values and Fornell-Larcker criterion established the convergent and discriminant validity, respectively. The concurrent validity of the tool was established through the statistically significant negative relationships between the A-DSMQ factors and HbA1C, in addition to its positive association with the practice of physical activity measured by the IPAQ. (4) Conclusions: Given the high EFA factor loadings, the CFA fit indices, the correlation matrix, the sensitivity analysis, the convergent validity, and the excellent internal consistency of the A-DSMQ, it can be concluded that the A-DSMQ is an effective psychometric tool for diabetes self-management in Tunisia.
Keywords: diabetes type 2; physical activity; reliability; self-management; validity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of the psychometric properties of the Persian version of the diabetes self-management questionnaire (DSMQ) in patients with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Jan 11;21(1):123-131. doi: 10.1007/s40200-021-00946-5. eCollection 2022 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 35673431 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric properties of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ) in Urdu.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017 Oct 12;15(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12955-017-0776-8. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017. PMID: 29025432 Free PMC article.
-
The Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (DSMQ): development and evaluation of an instrument to assess diabetes self-care activities associated with glycaemic control.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013 Aug 13;11:138. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-11-138. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2013. PMID: 23937988 Free PMC article.
-
Psychometric Properties of the Persian Version of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Iran.Int J Prev Med. 2021 Sep 29;12:120. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_241_19. eCollection 2021. Int J Prev Med. 2021. PMID: 34760131 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Diabetes Knowledge and Self-Management Among Portuguese Americans With Type 2 Diabetes.Public Health Nurs. 2025 May 16. doi: 10.1111/phn.13571. Online ahead of print. Public Health Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40377011 Review.
Cited by
-
The psychometric properties of the Diabetes Self-Efficacy Scale in Saudis with type 2 diabetes.Nurs Open. 2023 Sep;10(9):6408-6415. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1890. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 37319293 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation and Validation of the Italian Version of the Diabetes Self-Management Questionnaire (I-DSMQ) with an Additional Focus on Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Healthcare (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;13(5):475. doi: 10.3390/healthcare13050475. Healthcare (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40077037 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of self-management care and glycated hemoglobin level among diabetes mellitus patients attend diabetic center in armed forces hospital in southern region, Kingdom Saudi Arabia.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Jun;13(6):2425-2431. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1786_23. Epub 2024 Jun 14. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39027872 Free PMC article.
-
Glucometric parameter changes in patients with type 2 diabetes during ramadan fasting: A prospective comparative real-world study.Metabol Open. 2024 Jul 26;23:100304. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2024.100304. eCollection 2024 Sep. Metabol Open. 2024. PMID: 39175933 Free PMC article.
-
Rasch and Confirmatory Factor Analyses of the Arabic Version of the Diabetes Self-Management Scale (DSMS): An Intercultural Approach.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 22;11(1):35. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11010035. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niroomand M., Babaniamansour S., Aliniagerdroudbari E., Golshaian A., Meibodi A.M., Absalan A. Distress and depression among patients with diabetes mellitus: Prevalence and associated factors: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2021;20:141–151. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00721-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saad A.M., Younes Z., Abuali A., Farooqi M.H., Hassoun A.A. Diabetes distress and depression among patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes Endocr. Pract. 2021;4:182. doi: 10.4103/jdep.jdep_32_21. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

