A MLR-Based Approach to Analyze Regulators of T Lymphocyte Activation In Vivo
- PMID: 35628145
- PMCID: PMC9140849
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23105337
A MLR-Based Approach to Analyze Regulators of T Lymphocyte Activation In Vivo
Abstract
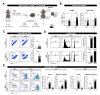
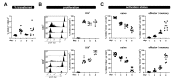
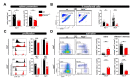
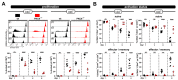
Depending on the context, robust and durable T lymphocyte activation is either desirable, as in the case of anti-tumor responses, or unwanted, in cases of autoimmunity when chronic stimulation leads to self-tissue damage. Therefore, reliable in vivo models are of great importance to identify and validate regulatory pathways of T lymphocyte activation. Here, we describe an in vivo mixed-lymphocyte-reaction (MLR) approach, which is based on the so-called parent-into-F1 (P → F1) mouse model in combination with the congenic marker CD45.1/2 and cell proliferation dye-labeling. This setup allows us to track adoptively transferred allogenic CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes and analyze their phenotype as well as the proliferation by flow cytometry in the blood and spleen. We could show hypo-reactive responses of T lymphocytes isolated from knockout mice with a known defect in T lymphocyte activation. Thus, this MLR-based in vivo model provides the opportunity to analyze positive regulators of T cell responses under physiological conditions of polyclonal T lymphocyte activation in vivo.
Keywords: GVHD model; MLR; T cell activation; allogenic response; in vivo model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Butyric acid derivative induces allospecific T cell anergy and prevents graft-versus-host disease.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003 Feb;25(1):13-27. doi: 10.1081/iph-120018280. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2003. PMID: 12675196
-
The role of dendritic cells as stimulators of minor lymphocyte-stimulating locus-specific T cell responses in the mouse. I. Differential capacity of dendritic cells to stimulate minor lymphocyte-stimulating locus-reactive T cell hybridomas and the primary anti-minor lymphocyte-stimulating locus mixed lymphocyte reaction.J Immunol. 1989 Feb 15;142(4):1069-78. J Immunol. 1989. PMID: 2464636
-
Radiosensitivity and responsiveness to recombinant interleukin-2 of effector cells of graft vs. host disease and mixed lymphocyte reaction in mice.Isr J Med Sci. 1992 Nov;28(11):767-72. Isr J Med Sci. 1992. PMID: 1468887
-
Quantifying the frequency of alloreactive T cells in vivo: new answers to an old question.J Immunol. 2001 Jan 15;166(2):973-81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.2.973. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11145675
-
Mechanisms of mouse T lymphocyte-induced suppression of the IgG2ab allotype and T lymphocyte tolerance to IgG2ab.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2001;49(6):407-15. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2001. PMID: 11814234 Review.
Cited by
-
T cell-intrinsic protein kinase D3 is dispensable for the cells' activation.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 17;13:1049033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1049033. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36466811 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

