Overlapping Features of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: From Genetics to Immunopathogenesis to Phenotypes
- PMID: 35628327
- PMCID: PMC9143118
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23105518
Overlapping Features of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: From Genetics to Immunopathogenesis to Phenotypes
Abstract
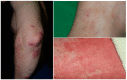
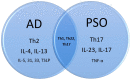
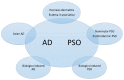
Psoriasis (PSO) and atopic dermatitis (AD) were once considered to be mutually exclusive diseases, but gradually regarded as a spectrum of disease. Shared genetic loci of both diseases were noted in some populations, including Chinese. Shared immunopathogenesis involving Th17, Th1, Th22 cells, or even IL-13 was found in certain stages or phenotypes. This review discusses the overlapping genetic susceptibility, shared cytokines, immune-mediated comorbidities, and clinical presentations. Overlapping conditions could be classified into mainly PSO lesions with AD features or vice versa, concomitant PSO and AD, or disease transformation as a result of biologics treatment.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; concomitant; overlap; paradoxical; psoriasis; psoriasis dermatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Tsen-fang Tsai has conducted clinical trials or received honoraria for serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Galderma, GSK-Stiefel, Janssen-Cilag, Leo-Pharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer Inc., and UCB Pharma. Ya-chu Tsai has delivered speeches held by AbbVie, Eli Lilly, Janssen-Cilag, Leo-Pharma, Novartis, and Pfizer.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

