Osteosarcopenia: A Narrative Review on Clinical Studies
- PMID: 35628399
- PMCID: PMC9147376
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23105591
Osteosarcopenia: A Narrative Review on Clinical Studies
Abstract
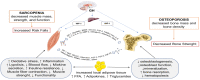
Osteosarcopenia (OS) is defined by the concurrent presence of osteopenia/osteoporosis and sarcopenia. The pathogenesis and etiology of OS involve genetic, biochemical, mechanical, and lifestyle factors. Moreover, an inadequate nutritional status, such as low intake of protein, vitamin D, and calcium, and a reduction in physical activity are key risk factors for OS. This review aims to increase knowledge about diagnosis, incidence, etiology, and treatment of OS through clinical studies that treat OS as a single disease. Clinical studies show the relationship between OS and the risk of frailty, falls, and fractures and some association with Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) pathologies such as diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. In some cases, the importance of deepening the related mechanisms is emphasized. Physical exercise with adequate nutrition and nutritional supplementations such as proteins, Vitamin D, or calcium, represent a significant strategy for breaking OS. In addition, pharmacological interventions may confer benefits on muscle and bone health. Both non-pharmacological and pharmacological interventions require additional randomized controlled trials (RCT) in humans to deepen the synergistic effect of exercise, nutritional interventions, and drug compounds in osteosarcopenia.
Keywords: clinical studies; interventions; osteosarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan S.J., Pham T.N., Arbabi S., Gross J.A., Damodarasamy M., Bentov I., Taitsman L.A., Mitchell S.H., Reed M.J. Associationof radiologic indicators of frailty with 1-year mortality in older trauma patients: Opportunistic screening for sarcopenia and os-teopenia. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:e164604. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2016.4604. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cruz-Jentoft A.J., Baeyens J.P., Bauer J.M., Boirie Y., Cederholm T., Landi F., Martin F.C., Michel J., Rolland Y., Schneider S.M., et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing. 2010;39:412–423. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afq034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical