Chemogenetic Depletion of Hypophysiotropic GnRH Neurons Does Not Affect Fertility in Mature Female Zebrafish
- PMID: 35628411
- PMCID: PMC9143870
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23105596
Chemogenetic Depletion of Hypophysiotropic GnRH Neurons Does Not Affect Fertility in Mature Female Zebrafish
Abstract
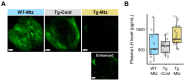
The hypophysiotropic gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and its neurons are crucial for vertebrate reproduction, primarily in regulating luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion and ovulation. However, in zebrafish, which lack GnRH1, and instead possess GnRH3 as the hypophysiotropic form, GnRH3 gene knockout did not affect reproduction. However, early-stage ablation of all GnRH3 neurons causes infertility in females, implicating GnRH3 neurons, rather than GnRH3 peptides in female reproduction. To determine the role of GnRH3 neurons in the reproduction of adult females, a Tg(gnrh3:Gal4ff; UAS:nfsb-mCherry) line was generated to facilitate a chemogenetic conditional ablation of GnRH3 neurons. Following ablation, there was a reduction of preoptic area GnRH3 neurons by an average of 85.3%, which was associated with reduced pituitary projections and gnrh3 mRNA levels. However, plasma LH levels were unaffected, and the ablated females displayed normal reproductive capacity. There was no correlation between the number of remaining GnRH3 neurons and reproductive performance. Though it is possible that the few remaining GnRH3 neurons can still induce an LH surge, our findings are consistent with the idea that GnRH and its neurons are likely dispensable for LH surge in zebrafish. Altogether, our results resurrected questions regarding the functional homology of the hypophysiotropic GnRH1 and GnRH3 in controlling ovulation.
Keywords: GnRH; LH; fertility; ovulation; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
GnRH-Gonadotropes Interactions Revealed by Pituitary Single-cell Transcriptomics in Zebrafish.Endocrinology. 2024 Oct 30;165(12):bqae151. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae151. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39499852 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted gonadotropin-releasing hormone-3 neuron ablation in zebrafish: effects on neurogenesis, neuronal migration, and reproduction.Endocrinology. 2010 Jan;151(1):332-40. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0548. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 19861502
-
Targeted Mutagenesis of the Hypophysiotropic Gnrh3 in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Reveals No Effects on Reproductive Performance.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 29;11(6):e0158141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158141. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27355207 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple gonadotropin-releasing hormone systems in non-mammalian vertebrates: Ontogeny, anatomy, and physiology.J Neuroendocrinol. 2022 May;34(5):e13068. doi: 10.1111/jne.13068. Epub 2021 Dec 21. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 34931380 Review.
-
The zebrafish as a model system for forebrain GnRH neuronal development.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009 Nov-Dec;164(2-3):151-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.01.012. Epub 2009 Jan 31. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19523393 Review.
Cited by
-
GnRH-Gonadotropes Interactions Revealed by Pituitary Single-cell Transcriptomics in Zebrafish.Endocrinology. 2024 Oct 30;165(12):bqae151. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae151. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 39499852 Free PMC article.
-
The satiety hormone cholecystokinin gates reproduction in fish by controlling gonadotropin secretion.Elife. 2024 Dec 24;13:RP96344. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96344. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39717899 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal dynamics reveal a stimulatory role for secretoneurin in zebrafish ovulation.PNAS Nexus. 2025 Apr 4;4(4):pgaf097. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgaf097. eCollection 2025 Apr. PNAS Nexus. 2025. PMID: 40191135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chan Y.-M., de Guillebon A., Lang-Muritano M., Plummer L., Cerrato F., Tsiaras S., Gaspert A., Lavoie H.B., Wu C.-H., Crowley W.F., et al. GNRH1 mutations in patients with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:11703–11708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903449106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

