Effectiveness of Dupilumab in the Treatment of Patients with Severe Uncontrolled CRSwNP: A "Real-Life" Observational Study in the First Year of Treatment
- PMID: 35628815
- PMCID: PMC9146210
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11102684
Effectiveness of Dupilumab in the Treatment of Patients with Severe Uncontrolled CRSwNP: A "Real-Life" Observational Study in the First Year of Treatment
Abstract
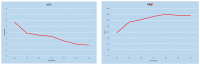
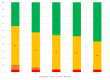
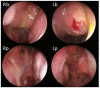
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of dupilumab in the treatment of severe uncontrolled Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP), with or without asthma as add-on therapy with intra-nasal corticosteroids in a real-life setting over the first year of treatment. Our data demonstrated that subcutaneous 300 mg dupilumab administered at home via a pre-filled auto-injector every two weeks, based on indications set by the Italian Medicines Agency, was rapidly effective in reducing the size of polyps, decreasing symptoms of disease, improving quality of life, and recovering olfaction. Significant improvement was observed after only 15 days of treatment, and it progressively increased at 6 and 12 months. Dupilumab was also effective in reducing the local nasal eosinophilic infiltrate, in decreasing the need for surgery and/or oral corticosteroids, and in improving control of associated comorbidities such as chronic eosinophilic otitis media and bronchial asthma. After 12 months of treatment, 96.5% of patients had a moderate/excellent response. From our data, it was evident that there was a group of patients that showed a very early response within one month of therapy, another group with early response within six months from baseline, and a last group that improved later within 12 months. The results of this study support the use of dupilumab as an effective option in the current standard of care for patients affected by severe uncontrolled CRSwNP.
Keywords: asthma; biologics; chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; dupilumab; eosinophilic otitis media; eosinophils; real life; treatment outcomes; type-2 inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- De Corso E., Lucidi D., Battista M., Romanello M., De Vita C., Baroni S., Autilio C., Galli J., Paludetti G. Prognostic value of nasal cytology and clinical factors in nasal polyps development in patients at risk: Can the beginning predict the end? Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017;7:861–867. doi: 10.1002/alr.21979. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hellings P., Akdis C., Bachert C., Bousquet J., Pugin B., Adriaensen G., Advani R., Agache I., Anjo C., Anmolsingh R., et al. EUFOREA Rhinology Research Forum 2016: Report of the brainstorming sessions on needs and priorities in rhinitis and rhinosinusitis. Rhinol. J. 2017;55:202–210. doi: 10.4193/Rhin17.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bachert C., Han J.K., Wagenmann M., Hosemann W., Lee S.E., Backer V., Mullol J., Gevaert P., Klimek L., Prokopakis E., et al. EUFOREA expert board meeting on uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and biologics: Definitions and management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021;147:29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.11.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Corso E., Bellocchi G., De Benedetto M., Lombardo N., Macchi A., Malvezzi L., Motta G., Pagella F., Vicini C., Passali D. Biologics for severe uncontrolled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A change management approach. Consensus of the Joint Committee of Italian Society of Otorhinolaryngology on biologics in rhinology. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022;42:1–16. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N1614. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

