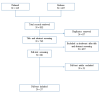
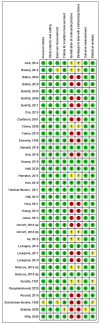
Drug-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions Leading to Emergency Department: Original Data and Systematic Review
- PMID: 35628936
- PMCID: PMC9143688
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11102811
Drug-Related Hypersensitivity Reactions Leading to Emergency Department: Original Data and Systematic Review
Abstract
The aim of the present study is to describe pharmacological characteristics of drug-related allergies and anaphylaxis leading to the emergency department (ED). An 8-year post hoc analysis on the MEREAFaPS Study database was performed (2012−2019). Subjects who experienced drug-related hypersensitivity leading to an ED visit were selected. Logistic regression analyses were used to estimate the reporting odds ratios (RORs) of drug-related allergies and anaphylaxis adjusting for sex, age classes, and ethnicity. In addition, a systematic review of observational studies evaluating drug-related hypersensitivity reactions leading to ED visits in outpatients was performed. Out of 94,073 ED visits, 14.4% cases were drug-related allergies and 0.6% were anaphylaxis. Females accounted for 56%. Multivariate logistic regression showed a higher risk of drug-related allergy among males and all age classes < 65 years, while a higher risk of anaphylaxis was observed for females (ROR 1.20 [1.01−1.42]) and adults (ROR 2.63 [2.21−3.14]). The systematic review included 37 studies. ED visits related to allergy and anaphylaxis ranged from 0.004% to 88%, and drug-related allergies and anaphylaxis ranged from 0.007% to 88%. Both in our analysis and in primary studies, antibacterials, analgesics, and radiocontrast agents were identified as the most common triggers of hypersensitivity.
Keywords: anaphylaxis; drug allergy; emergency department; hospitalization; hypersensitivity; pharmacovigilance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Cardona V., Ansotegui I.J., Ebisawa M., El-Gamal Y., Fernandez Rivas M., Fineman S., Geller M., Gonzalez-Estrada A., Greenberger P.A., Borges M.S., et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020;13:100472. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100472. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources