The Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance-A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 35628992
- PMCID: PMC9147423
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11102866
The Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance-A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
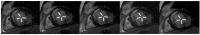
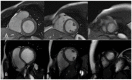
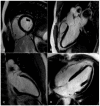
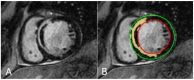
Cardiovascular disease remains an integral field on which new research in both the biomedical and technological fields is based, as it remains the leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. However, despite the progress of cardiac imaging techniques, the heart remains a challenging organ to study. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as one of the major innovations in the field of diagnostic imaging, with a dramatic impact on cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging (CMR). AI will be increasingly present in the medical world, with strong potential for greater diagnostic efficiency and accuracy. Regarding the use of AI in image acquisition and reconstruction, the main role was to reduce the time of image acquisition and analysis, one of the biggest challenges concerning magnetic resonance; moreover, it has been seen to play a role in the automatic correction of artifacts. The use of these techniques in image segmentation has allowed automatic and accurate quantification of the volumes and masses of the left and right ventricles, with occasional need for manual correction. Furthermore, AI can be a useful tool to directly help the clinician in the diagnosis and derivation of prognostic information of cardiovascular diseases. This review addresses the applications and future prospects of AI in CMR imaging, from image acquisition and reconstruction to image segmentation, tissue characterization, diagnostic evaluation, and prognostication.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; cardiac magnetic resonance; deep learning; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Pontone G., Andreini D., Bertella E., Baggiano A., Mushtaq S., Loguercio M., Segurini C., Conte E., Beltrama V., Annoni A., et al. Impact of an intra-cycle motion correction algorithm on overall evaluability and diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography coronary angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2016;26:147–156. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3793-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guaricci A.I., Maffei E., Brunetti N.D., Montrone D., Di Biase L., Tedeschi C., Gentile G., Macarini L., Midiri M., Cademartiri F., et al. Heart rate control with oral ivabradine in computed tomography coronary angiography: A randomized comparison of 7.5 mg vs 5 mg regimen. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013;168:362–368. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.09.041. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pontone G., Weir-McCall J.R., Baggiano A., Del Torto A., Fusini L., Guglielmo M., Muscogiuri G., Guaricci A.I., Andreini D., Patel M., et al. Determinants of Rejection Rate for Coronary CT Angiography Fractional Flow Reserve Analysis. Radiology. 2019;292:597–605. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019182673. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pontone G., Andreini D., Guaricci A.I., Guglielmo M., Baggiano A., Muscogiuri G., Fusini L., Soldi M., Fazzari F., Berzovini C., et al. Quantitative vs. qualitative evaluation of static stress computed tomography perfusion to detect haemodynamically significant coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2018;19:1244–1252. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jey111. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

