SBRT for Localized Prostate Cancer: CyberKnife vs. VMAT-FFF, a Dosimetric Study
- PMID: 35629378
- PMCID: PMC9144859
- DOI: 10.3390/life12050711
SBRT for Localized Prostate Cancer: CyberKnife vs. VMAT-FFF, a Dosimetric Study
Abstract
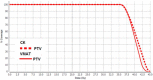
In recent years, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) has gained popularity among clinical methods for the treatment of medium and low risk prostate cancer (PCa), mainly as an alternative to surgery. The hypo-fractionated regimen allows the administration of high doses of radiation in a small number of fractions; such a fractionation is possible by exploiting the different intrinsic prostate radiosensitivity compared with the surrounding healthy tissues. In addition, SBRT treatment guaranteed a better quality of life compared with surgery, avoiding risks, aftermaths, and possible complications. At present, most stereotactic prostate treatments are performed with the CyberKnife (CK) system, which is an accelerator exclusively dedicated for stereotaxis and it is not widely spread in every radiotherapy centre like a classic linear accelerator (LINAC). To be fair, a stereotactic treatment is achievable also by using a LINAC through Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT), but some precautions must be taken. The aim of this work is to carry out a dosimetric comparison between these two methodologies. In order to pursue such a goal, two groups of patients were selected at Instituto Nazionale Tumori-IRCCS Fondazione G. Pascale: the first group consisting of ten patients previously treated with a SBRT performed with CK; the second one was composed of ten patients who received a hypo-fractionated VMAT treatment and replanned in VMAT-SBRT flattening filter free mode (FFF). The two SBRT techniques were rescaled at the same target coverage and compared by normal tissue sparing, dose distribution parameters and delivery time. All organs at risk (OAR) constraints were achieved by both platforms. CK exhibits higher performances in terms of dose delivery; nevertheless, the general satisfying dosimetric results and the significantly shorter delivery time make VMAT-FFF an attractive and reasonable alternative SBRT technique for the treatment of localized prostate cancer.
Keywords: CyberKnife; SBRT; VMAT; flattening filter free; hypofractionation; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- AIOM . I Numeri del Cancro in Italia, 2021. AIOM Associazione Italiana di Oncologia Medica; Milano, Italy: 2021.
-
- Leslie S.W., Soon-Sutton T.L., Sajjad H., Siref L.E. Prostate Cancer. Stat Pearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

