Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Progressive Damage of Reinforced Concrete T-Beams under Four-Point Bending
- PMID: 35629513
- PMCID: PMC9147450
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15103486
Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Progressive Damage of Reinforced Concrete T-Beams under Four-Point Bending
Abstract
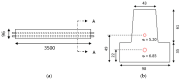
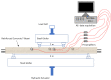
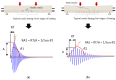
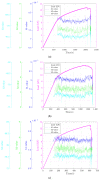
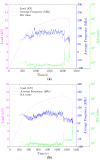
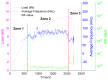
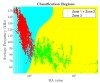
Acoustic Emission (AE) is revealed to be highly adapted to monitor materials and structures in materials research and for site monitoring. AE-features can be either analyzed by means of physical considerations (geophysics/seismology) or through their time/frequency waveform characteristics. However, the multitude of definitions related to the different parameters as well as the processing methods makes it necessary to develop a comparative analysis in the case of a heterogeneous material such as civil engineering concrete. This paper aimed to study the micro-cracking behavior of steel fiber-reinforced reinforced concrete T-beams subjected to mechanical tests. For this purpose, four-points bending tests, carried out at different displacement velocities, were performed in the presence of an acoustic emission sensors network. Besides, a comparison between the sensitivity to damage of three definitions corresponding to the b-value parameter was performed and completed by the evolution of the RA-value and average frequency (AF) as a function of loading time. This work also discussed the use of the support-vector machine (SVM) approach to define different damage zones in the load-displacement curve. This work shows the limits of this approach and proposes the use of an unsupervised learning approach to cluster AE data according to physical and time/frequency parameters. The paper ends with a conclusion on the advantages and limitations of the different methods and parameters used in connection with the micro/macro tensile and shear mechanisms involved in concrete cracking for the purpose of in situ monitoring of concrete structures.
Keywords: RA-value; acoustic emission (AE); average frequency; b-value; four-point bending; reinforced concrete beam; support-vectors machine; unsupervised machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Prem P.R., Murthy A.R. Acoustic emission monitoring of reinforced concrete beams subjected to four-point-bending. Appl. Acoust. 2017;117:28–38. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2016.08.006. - DOI
-
- Wevers M. Listening to the sound of materials: Acoustic emission for the analysis of material behaviour. NDT E Int. 1997;30:99–106. doi: 10.1016/S0963-8695(96)00051-5. - DOI
-
- Grosse C.U., Ohtsu M., editors. Acoustic Emission Testing—Basics for Research—Applications in Civil Engineering. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2008.
-
- Dzaye E.D., De Schutter G., Aggelis D.G. Study on mechanical acoustic emission sources in fresh concrete. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018;18:742–754. doi: 10.1016/j.acme.2017.12.004. - DOI
-
- An Y.K., Kim M.K., Sohn H. Piezoelectric transducers for assessing and monitoring civil infrastructures. Sens. Technol. Civ. Infrastruct. 2014;1:86–120.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

