Liquid Superlubricity Enabled by the Synergy Effect of Graphene Oxide and Lithium Salts
- PMID: 35629573
- PMCID: PMC9143536
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15103546
Liquid Superlubricity Enabled by the Synergy Effect of Graphene Oxide and Lithium Salts
Abstract
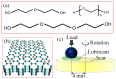
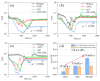
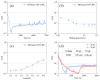
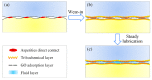
In this study, graphene oxide (GO) nanoflakes and lithium salt (LiPF6) were utilized as lubrication additives in ether bond-containing dihydric alcohol aqueous solutions (DA(aq)) to improve lubrication performances. The apparent friction reduction and superlubricity were realized at the Si3N4/sapphire interface. The conditions and laws for superlubricity realization have been concluded. The underlying mechanism was the synergy effect of GO and LiPF6. It was proven that a GO adsorption layer was formed at the interface, which caused the shearing interface to transfer from solid asperities to GO interlayers (weak interlayer interactions), resulting in friction reduction and superlubricity realization. In addition to the GO adsorption layer, a boundary layer containing phosphates and fluorides was formed by tribochemical reactions of LiPF6 and was conducive to low friction. Additionally, a fluid layer contributed to friction reduction as well. This work proved that GO-family materials are promising for friction reduction, and provided new insights into realizing liquid superlubricity at macroscale by combining GO with other materials.
Keywords: LiPF6; friction reduction; graphene oxide; superlubricity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Luo J.B., Liu M., Ma L.R. Origin of friction and the new frictionless technology—Superlubricity: Advancements and future outlook. Nano Energy. 2021;86:106092. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106092. - DOI
-
- Fan M.J., Liang Y.M., Zhou F., Liu W. Dramatically improved friction reduction and wear resistance by in situ formed ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2012;2:6824–6830. doi: 10.1039/c2ra20888a. - DOI
-
- Erdemir A., Martin J.M., Luo J.B. Superlubricity. 2nd ed. Elsevier Science; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020.
-
- Yu G.M., Gong Z.B., Jiang B., Wang D., Bai C., Zhang J. Superlubricity for hydrogenated diamond like carbon induced by thin MoS2 and DLC layer in moist air. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020;102:107668. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2019.107668. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

