Is the Pendulum of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance Swinging Back after COVID-19?
- PMID: 35630400
- PMCID: PMC9146770
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10050957
Is the Pendulum of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance Swinging Back after COVID-19?
Abstract
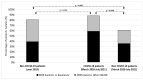
The COVID-19 pandemic may have had an effect on antimicrobial resistance. We compared the prevalence of ESKAPE multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections in COVID-19 affected/unaffected patients admitted to intensive care units (ICU) or infectious disease units at the "Mater Domini" University Hospital of Catanzaro between 1 March 2020 and 31 July 2021. Moreover, an analysis of MDR rates in ICU comparing the pre-pandemic period with the pandemic period was performed, and the possible consequence on in-hospital mortality was explored. One hundred and eighty-four ESKAPE isolates were analyzed from 362 SARS-CoV-2 positive and 199 negative patients. In total, 116 out of 171 Gram-negative isolates were classified as MDR, and a higher frequency was observed in COVID-19 compared with non-COVID-19 patients (74.2% vs. 60.3%; p = 0.052). A higher rate of MDR ESKAPE bacteria was observed in COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU compared with COVID-19 unaffected patients admitted to the same ward in 2019 (88% vs. 80.4%; p = 0.186). Acinetobacter baumannii was the main pathogen in COVID-19 patients (58.7%), where it was the most frequent cause of bloodstream infection with the highest mortality rate (68.7%). Increase in MDR appeared to be associated with COVID-19 but only in the ICU setting. Acinetobacter baumannii was associated with the risk of death, indicating the importance of implementing infection control measures urgently.
Keywords: COVID-19; MDR; antimicrobial resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Karruli A., Boccia F., Gagliardi M., Patauner F., Ursi M.P., Sommese P., De Rosa R., Murino P., Ruocco G., Corcione A., et al. Multidrug-Resistant Infections and Outcome of Critically Ill Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Single Center Experience. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021;27:1167–1175. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0489. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-Jácome L.E., Fernández-Rodríguez D., Franco-Cendejas R., Camacho-Ortiz A., Morfin-Otero M., Rodríguez-Noriega E., Ponce-de-León A., Ortiz-Brizuela E., Rojas-Larios F., Velázquez-Acosta M., et al. Increment Antimicrobial Resistance During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results from the Invifar Network. Microb. Drug. Resist. 2022;28:338–345. - PubMed
-
- Patel A., Emerick M., Cabunoc M.K., Williams M.H., Preas M.A., Schrank G., Rabinowitz R., Luethy P., Johnson J.K., Leekha S. Rapid Spread and Control of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria in COVID-19 Patient Care Units. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021;27:1234–1237. doi: 10.3201/eid2704.204036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Badulak J., Antonini M.V., Stead C.M., Shekerdemian L., Raman L., Paden M.L., Agerstrand C., Bartlett R.H., Barrett N., Combes A., et al. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19: Updated 2021 Guidelines from the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization. ASAIO J. 2021;67:485–495. doi: 10.1097/MAT.0000000000001422. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

