Functional Foods, Nutraceuticals and Probiotics: A Focus on Human Health
- PMID: 35630507
- PMCID: PMC9143759
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10051065
Functional Foods, Nutraceuticals and Probiotics: A Focus on Human Health
Abstract
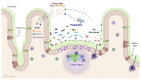
Functional foods are classified as traditional or staple foods that provide an essential nutritional level and share potentially positive effects on host health, including the reduction of disease by optimizing the immune system's ability to prevent and control infections by pathogens, as well as pathologies that cause functional alterations in the host. This chapter reviews the most recent research and advances in this area and discusses some perspectives on what the future holds in this area.
Keywords: functional foods; lactic acid bacteria; microbiota; nutraceuticals; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hill C., Guarner F., Reid G., Gibson G.R., Merenstein D.J., Pot B., Morelli L., Canani R.B., Flint H.J., Salminen S., et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014;11:506–514. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2014.66. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases