Design, Synthesis, Bioactivity Evaluation, Crystal Structures, and In Silico Studies of New α-Amino Amide Derivatives as Potential Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors
- PMID: 35630812
- PMCID: PMC9147695
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27103335
Design, Synthesis, Bioactivity Evaluation, Crystal Structures, and In Silico Studies of New α-Amino Amide Derivatives as Potential Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors
Abstract
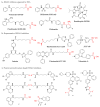
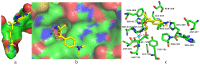
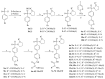
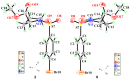
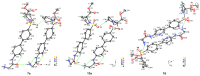
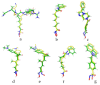
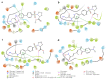
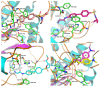
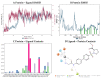
Hydroxamate, as a zinc-binding group (ZBG), prevails in the design of histone deacetylase 6(HDAC6) inhibitors due to its remarkable zinc-chelating capability. However, hydroxamate-associated genotoxicity and mutagenicity have limited the widespread application of corresponding HDAC6 inhibitors in the treatment of human diseases. To avoid such side effects, researchers are searching for novel ZBGs that may be used for the synthesis of HDAC6 inhibitors. In this study, a series of stereoisomeric compounds were designed and synthesized to discover non-hydroxamate HDAC6 inhibitors using α-amino amide as zinc-ion-chelating groups, along with a pair of enantiomeric isomers with inverted L-shaped vertical structure as cap structures. The anti-proliferative activities were determined against HL-60, Hela, and RPMI 8226 cells, and 7a and its stereoisomer 13a exhibited excellent activities against Hela cells with IC50 = 0.31 µM and IC50 = 5.19 µM, respectively. Interestingly, there is a significant difference between the two stereoisomers. Moreover, an evaluation of cytotoxicity toward human normal liver cells HL-7702 indicated its safety for normal cells. X-ray single crystal diffraction was employed to increase insights into molecule structure and activities. It was found that the carbonyl of the amide bond is on the different side from the amino and pyridine nitrogen atoms. To identify possible protein targets to clarify the mechanism of action and biological activity of 7a, a small-scale virtual screen using reverse docking for HDAC isoforms (1-10) was performed and the results showed that HDAC6 was the best receptor for 7a, suggesting that HDAC6 may be a potential target for 7a. The interaction pattern analysis showed that the α-amino amide moiety of 7a coordinated with the zinc ion of HDAC6 in a bidentate chelate manner, which is similar to the chelation pattern of hydroxamic acid. Finally, the molecular dynamics simulation approaches were used to assess the docked complex's conformational stability. In this work, we identified 7a as a potential HDAC6 inhibitor and provide some references for the discovery of non-hydroxamic acid HDAC6 inhibitors.
Keywords: HDAC6 inhibitors; bioactivity evaluation; crystal structure; molecular dynamics simulation; non-hydroxamate; reverse docking; synthesis; α-amino amide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
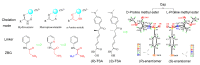
Similar articles
-
Identification of Novel Histone Deacetylase 6-Selective Inhibitors Bearing 3,3,3-Trifluorolactic Amide (TFLAM) Motif as a Zinc Binding Group.Chembiochem. 2021 Nov 16;22(22):3158-3163. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202100255. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Chembiochem. 2021. PMID: 34224197
-
Recent advances in the discovery of potent and selective HDAC6 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:1406-1418. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.10.040. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29133060 Review.
-
Fragment-Based Drug Design of Selective HDAC6 Inhibitors.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2266:155-170. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1209-5_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33759126
-
Synthesis and Biological Investigation of Oxazole Hydroxamates as Highly Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2016 Feb 25;59(4):1545-55. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b01493. Epub 2015 Dec 22. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26653328
-
Mercaptoacetamide: A promising zinc-binding group for the discovery of selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 1;209:112887. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112887. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33035922 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small molecules in the treatment of COVID-19.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 5;7(1):387. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36464706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis, biological and in silico evaluation of 3‑carboxy‑coumarin sulfonamides as potential antiproliferative agents targeting HDAC6.Biomed Rep. 2024 Oct 30;22(1):6. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1884. eCollection 2025 Jan. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 39559821 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

