The Graphene Structure's Effects on the Current-Voltage and Photovoltaic Characteristics of Directly Synthesized Graphene/n-Si(100) Diodes
- PMID: 35630863
- PMCID: PMC9147930
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12101640
The Graphene Structure's Effects on the Current-Voltage and Photovoltaic Characteristics of Directly Synthesized Graphene/n-Si(100) Diodes
Abstract
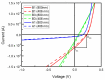
Graphene was synthesized directly on Si(100) substrates by microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (MW-PECVD). The effects of the graphene structure on the electrical and photovoltaic properties of graphene/n-Si(100) were studied. The samples were investigated using Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, and by measuring current-voltage (I-V) graphs. The temperature of the hydrogen plasma annealing prior to graphene synthesis was an essential parameter regarding the graphene/Si contact I-V characteristics and photovoltaic parameters. Graphene n-type self-doping was found to occur due to the native SiO2 interlayer at the graphene/Si junction. It was the prevalent cause of the significant decrease in the reverse current and short-circuit current. No photovoltaic effect dependence on the graphene roughness and work function could be observed.
Keywords: MW-PECVD; graphene; photovoltaics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Bonaccorso F., Sun Z., Hasan T., Ferrari A.C. Graphene Photonics and Optoelectronics. Nat. Photonics. 2010;4:611–622. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.186. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

