Histopathologic Oral Cancer Prediction Using Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Biopsy Empowered with Transfer Learning
- PMID: 35632242
- PMCID: PMC9146317
- DOI: 10.3390/s22103833
Histopathologic Oral Cancer Prediction Using Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Biopsy Empowered with Transfer Learning
Abstract
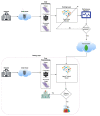
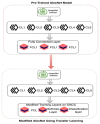
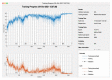
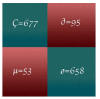
Oral cancer is a dangerous and extensive cancer with a high death ratio. Oral cancer is the most usual cancer in the world, with more than 300,335 deaths every year. The cancerous tumor appears in the neck, oral glands, face, and mouth. To overcome this dangerous cancer, there are many ways to detect like a biopsy, in which small chunks of tissues are taken from the mouth and tested under a secure and hygienic microscope. However, microscope results of tissues to detect oral cancer are not up to the mark, a microscope cannot easily identify the cancerous cells and normal cells. Detection of cancerous cells using microscopic biopsy images helps in allaying and predicting the issues and gives better results if biologically approaches apply accurately for the prediction of cancerous cells, but during the physical examinations microscopic biopsy images for cancer detection there are major chances for human error and mistake. So, with the development of technology deep learning algorithms plays a major role in medical image diagnosing. Deep learning algorithms are efficiently developed to predict breast cancer, oral cancer, lung cancer, or any other type of medical image. In this study, the proposed model of transfer learning model using AlexNet in the convolutional neural network to extract rank features from oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) biopsy images to train the model. Simulation results have shown that the proposed model achieved higher classification accuracy 97.66% and 90.06% of training and testing, respectively.
Keywords: AlexNet; angiogenic; artificial intelligence; machine learning; malignant; medical imaging; neural network; oral cancer; oral squamous cell carcinoma; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Report on Cancer: Setting Priorities, Investing Wisely and Providing Care for All. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020. Technical Report.
-
- Lavanya L., Chandra J. Oral Cancer Analysis Using Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2019;12:596–601.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

