Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity
- PMID: 35632683
- PMCID: PMC9143443
- DOI: 10.3390/v14050941
Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity
Abstract
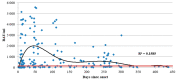
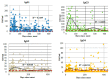
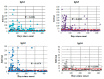
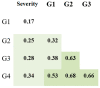
IgG is the most prominent marker of post-COVID-19 immunity. Not only does this subtype mark the late stages of infection, but it also stays in the body for a timespan of at least 6 months. However, different IgG subclasses have different properties, and their roles in specific anti-COVID-19 responses have yet to be determined. We assessed the concentrations of IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4 against different SARS-CoV-2 antigens (N protein, S protein RBD) using a specifically designed method and samples from 348 COVID-19 patients. We noted a statistically significant association between severity of COVID-19 infection and IgG concentrations (both total and subclasses). When assessing anti-N protein and anti-RBD IgG subclasses, we noted the importance of IgG3 as a subclass. Since it is often associated with early antiviral response, we presumed that the IgG3 subclass is the first high-affinity IgG antibody to be produced during COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; IgG; IgG subclasses; severity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 29 March 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Struyf T., Deeks J.J., Dinnes J., Takwoingi Y., Davenport C., Leeflang M.M., Spijker R., Hooft L., Emperador D., Dittrich S., et al. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease. Cochrane COVID-19, Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020;7:CD013665. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

