Distinct skin microbiome community structures in congenital ichthyosis
- PMID: 35633118
- PMCID: PMC10234690
- DOI: 10.1111/bjd.21687
Distinct skin microbiome community structures in congenital ichthyosis
Abstract
Background: The ichthyoses are rare genetic keratinizing disorders that share the characteristics of an impaired epidermal barrier and increased risk of microbial infections. Although ichthyotic diseases share a T helper (Th) 17 cell immune signature, including increased expression of antimicrobial peptides, the skin microbiota of ichthyoses is virtually unexplored.
Objectives: To analyse the metagenome profile of skin microbiome for major congenital ichthyosis subtypes.
Methods: Body site-matched skin surface samples were collected from the scalp, upper arm and upper buttocks of 16 healthy control participants and 22 adult patients with congenital forms of ichthyosis for whole metagenomics sequencing analysis.
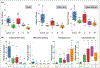
Results: Taxonomic profiling showed significant shifts in bacteria and fungi abundance and sporadic viral increases across ichthyosis subtypes. Cutibacterium acnes and Malassezia were significantly reduced across body sites, consistent with skin barrier disruption and depletion of lipids. Microbial richness was reduced, with specific increases in Staphylococcus and Corynebacterium genera, as well as shifts in fungal species, including Malassezia. Malassezia globosa was reduced at all body sites, whereas M. sympodialis was reduced in the ichthyotic upper arm and upper buttocks. Malassezia slooffiae, by contrast, was strikingly increased at all body sites in participants with congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE) and lamellar ichthyosis (LI). A previously undescribed Trichophyton species was also detected as sporadically colonizing the skin of patients with CIE, LI and epidermolytic ichthyosis subtypes.
Conclusions: The ichthyosis skin microbiome is significantly altered from healthy skin with specific changes predominating among ichthyosis subtypes. Skewing towards the Th17 pathway may represent a response to the altered microbial colonization in ichthyosis. What is already known about this topic? The skin microbiome of congenital ichthyoses is largely unexplored. Microbes play an important role in pathogenesis, as infections are common. The relative abundances of staphylococci and corynebacteria is increased in the cutaneous microbiome of patients with Netherton syndrome, but extension of these abundances to all congenital ichthyoses is unexplored. What does this study add? A common skin microbiome signature was observed across congenital ichthyoses. Distinct microbiome features were associated with ichthyosis subtypes. Changes in microbiome may contribute to T helper 17 cell immune polarization. What is the translational message? These data provide the basis for comparison of the microbiome with lipidomic and transcriptomic alterations in these forms of ichthyosis and consideration of correcting the dysbiosis as a therapeutic intervention.
© 2022 British Association of Dermatologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Impaired epidermal barriers in congenital ichthyoses house a changing microbial landscape.Br J Dermatol. 2022 Oct;187(4):457-458. doi: 10.1111/bjd.21746. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Br J Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35905982 No abstract available.
References
-
- Oji V, Tadini G, Akiyama M et al. Revised nomenclature and classification of inherited ichthyoses: results of the First Ichthyosis Consensus Conference in Soreze 2009. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010; 63:607–41. - PubMed
-
- Craig WY, Roberson M, Palomaki GE et al. Prevalence of steroid sulfatase deficiency in California according to race and ethnicity. Prenat Diagn 2010; 30:893–8. - PubMed
-
- Chavanas S, Bodemer C, Rochat A et al. Mutations in SPINK5, encoding a serine protease inhibitor, cause Netherton syndrome. Nat Genet 2000; 25:141–2. - PubMed

