Effect of Yifei-Huoxue Decoction Combined with Tiotropium on Inflammatory Cytokine Levels, Pulmonary Function, and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 35634054
- PMCID: PMC9135534
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5740181
Effect of Yifei-Huoxue Decoction Combined with Tiotropium on Inflammatory Cytokine Levels, Pulmonary Function, and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effect of Yifei-Huoxue Decoction Combined with Tiotropium on Inflammatory Cytokine Levels, Pulmonary Function, and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Dec 25;2022:9820914. doi: 10.1155/2022/9820914. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36597424 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: The main objective is to investigate the effect of Yifei-Huoxue decoction combined with tiotropium on the inflammatory cytokine levels, pulmonary function, and quality of life in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Methods: Ninety-eight COPD patients who were treated in our hospital from January 2021 to January 2022 were selected as the research objects, and they were divided into reference group (routine treatment) and study group (Yifei-Huoxue decoction combined with tiotropium), with 49 cases in each group. The patients' clinical indexes were compared between the two groups, and the clinical efficacy in the two groups was analyzed.
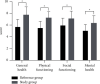
Results: Compared with the reference group, the study group had remarkably lower inflammatory cytokine levels (including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), C-reactive protein (CRP), and interleukin-6 (IL-6)) after treatment (P > 0.05). In terms of the patients' pulmonary function indexes after treatment, the study group achieved lower forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1s (FEV1), and FEV1/FVC levels compared with the reference group (P < 0.05). Both groups had a lower erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) after treatment compared with that before treatment. However, the intergroup difference in the ESRs after treatment was remarkable, and the study group had a much lower ESR compared with the reference group (P < 0.05). Compared with the reference group, the study group achieved much higher 36-item short form health survey (SF-36) scores in dimensions of general health, physical functioning, social functioning, and mental health after treatment (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Yifei-Huoxue decoction combined with tiotropium not only enhances the COPD patients' pulmonary function but also decreases their inflammatory levels. Therefore, this treatment is conducive to promoting the COPD patients' recovery and exerts positive effect on improving their quality of life.
Copyright © 2022 Yunjiao Sheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Hojo M., Saihara A., Taniguchi Y. Clinical usefulness of once-daily triple therapy ciclesonide and tiotropium bromide/olodaterol combination inhaler for COPD patients (2ND REPORT) Respirology . 2018;23(2):p. 242.
-
- Xiong X. f., Fan L. l., Wu H. x., Zhu M., Cheng D. y. Effects of tiotropium combined with theophylline on stable COPD patients of group B, D and its impact on small airway function: a randomized controlled trial. Advances in Therapy . 2018;35(12):2201–2213. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0831-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao D., Ling C., Guo Q., Jin J. H. Efficacy and safety of tiotropium bromide combined with budesonide/formoterol in the treatment of moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine . 2018;16(6):4578–4584. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6773. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan K. H., Tsoi Y. Y. S., Mccall M. The effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) as an adjunct treatment on stable COPD patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine . 2021;2021:23. doi: 10.1155/2021/5550332.5550332 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous