Breast Milk and the Importance of Chrononutrition
- PMID: 35634367
- PMCID: PMC9133889
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.867507
Breast Milk and the Importance of Chrononutrition
Abstract
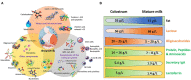
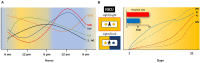
During pregnancy the human fetus receives timed cues from the circadian rhythms of temperature, metabolites, and hormones from the mother. This influence is interrupted after parturition, the infant does not secrete melatonin and their circadian rhythms are still immature. However, evolution provided the solution to this problem. The newborn can continue receiving the mother's timed cues through breastmilk. Colostrum, transitional, and mature human milk are extraordinary complex biofluids that besides nutrients, contain an array of other non-nutritive components. Upon birth the first milk, colostrum, is rich in bioactive, immunological factors, and in complex oligosaccharides which help the proper establishment of the microbiome in the gut, which is crucial for the infants' health. Hormones, such as glucocorticoids and melatonin, transfer from the mother's plasma to milk, and then the infant is exposed to circadian cues from their mother. Also, milk components of fat, proteins, amino acids, and endogenous cannabinoids, among others, have a markedly different concentration between day and night. In the present review, we give an overview of nutritive and non-nutritive components and their daily rhythms in human milk and explore their physiological importance for the infant. Finally, we highlight some interventions with a circadian approach that emphasize the importance of circadian rhythms in the newborn for their survival, proper growth, and development. It is estimated that ~600,000 deaths/year are due to suboptimal breastfeeding. It is advisable to increase the rate of exclusive breastfeeding, during the day and night, as was established by the evolution of our species.
Keywords: cannabinoids; chrononutrition; circadian feeding; glucocorticoids; melatonin; oligosaccharides; secretory IgA; tryptophan.
Copyright © 2022 Caba-Flores, Ramos-Ligonio, Camacho-Morales, Martínez-Valenzuela, Viveros-Contreras and Caba.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

