A Comprehensive Comparison of Different Selenium Supplements: Mitigation of Heat Stress and Exercise Fatigue-Induced Liver Injury
- PMID: 35634369
- PMCID: PMC9133842
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.917349
A Comprehensive Comparison of Different Selenium Supplements: Mitigation of Heat Stress and Exercise Fatigue-Induced Liver Injury
Abstract
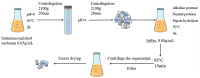
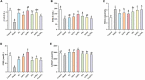
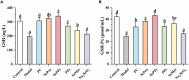
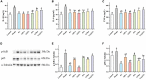
This study aimed to compare the protective effects of different selenium supplements against heat stress and exercise fatigue-induced liver injury and to investigate the potential mechanisms of action. Selenium-enriched soybean protein (SePro), selenium-enriched soybean peptides (SePPs), and selenomethionine (SeMet) are organic selenium supplements in which selenium replaces the sulfur in their sulfur-containing amino acids. Common peptides (PPs) are obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean protein which was extracted from common soybean. The SePPs with higher hydrolysis degree and selenium retention were isolated via alkaline solubilization and acid precipitation and the enzymatic hydrolysis of alkaline protease, neutral protease, and papain. The results showed that SePPs could significantly increase the antioxidant levels in rats, inhibit lipid peroxidation, and reduce liver enzyme levels in rat serum, while the histological findings indicated that the inflammatory cell infiltration in the liver tissue was reduced, and new cells appeared after treatment with SePPs. Moreover, SePPs could increase glutathione (GSH) and GSH peroxidase (GSH-Px) in the liver, as well as protect the liver by regulating the NF-κB/IκB pathway, prevent interleukin 1β (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) release in the liver. The SePPs displayed higher antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity in vivo than SePro, SeMet, Sodium selenite (Na2SeO3), and PPs. Therefore, SePPs could be used as a priority selenium resource to develop heatstroke prevention products or nutritional supplements.
Keywords: exercise fatigue; heat stress; heatstroke; inflammation; oxidative damage; selenium-enriched soybean peptides.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhang, Li, Liu, Xi and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Selenium-containing soybean antioxidant peptides: Preparation and comprehensive comparison of different selenium supplements.Food Chem. 2021 Oct 1;358:129888. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129888. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33933969
-
Selenium-enriched peptides identified from selenium-enriched soybean protein hydrolysate: protective effects against heat damage in Caco-2 cells.Food Funct. 2023 Aug 29;14(17):7882-7896. doi: 10.1039/d3fo01103h. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 37489104
-
Effects of different drying methods on the structure, bioaccessibility, and bioavailability of selenium-enriched peptides from soybean sprouts.Food Chem. 2025 Mar 15;468:142442. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142442. Epub 2024 Dec 10. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 39671918
-
Role of selenium toxicity and oxidative stress in aquatic birds.Aquat Toxicol. 2002 Apr;57(1-2):11-26. doi: 10.1016/s0166-445x(01)00263-6. Aquat Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 11879935 Review.
-
Selenium-Containing Proteins/Peptides from Plants: A Review on the Structures and Functions.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Dec 23;68(51):15061-15073. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c05594. Epub 2020 Dec 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 33315396 Review.
Cited by
-
Auricularia auricula Peptides Nutritional Supplementation Delays H2O2-Induced Senescence of HepG2 Cells by Modulation of MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 25;15(17):3731. doi: 10.3390/nu15173731. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686763 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Function of Plant-Derived Bioactive Peptides: A Review.Foods. 2022 Aug 6;11(15):2361. doi: 10.3390/foods11152361. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35954128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium and Skeletal Muscle Health in Sports Nutrition.Nutrients. 2025 May 31;17(11):1902. doi: 10.3390/nu17111902. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Lonicera japonica Extract with Different Contents of Chlorogenic Acid on Lactation Performance, Serum Parameters, and Rumen Fermentation in Heat-Stressed Holstein High-Yielding Dairy Cows.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 22;14(8):1252. doi: 10.3390/ani14081252. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672400 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouted Black Quinoa Extract Alleviates Heat Stress-Induced Liver Injury in Rats by Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway.Foods. 2025 Aug 8;14(16):2758. doi: 10.3390/foods14162758. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40870671 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

