Preparation of image databases for artificial intelligence algorithm development in gastrointestinal endoscopy
- PMID: 35636749
- PMCID: PMC9539300
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2021.229
Preparation of image databases for artificial intelligence algorithm development in gastrointestinal endoscopy
Abstract
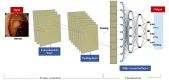
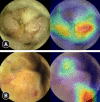
Over the past decade, technological advances in deep learning have led to the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging. The most commonly used structure in image recognition is the convolutional neural network, which mimics the action of the human visual cortex. The applications of AI in gastrointestinal endoscopy are diverse. Computer-aided diagnosis has achieved remarkable outcomes with recent improvements in machine-learning techniques and advances in computer performance. Despite some hurdles, the implementation of AI-assisted clinical practice is expected to aid endoscopists in real-time decision-making. In this summary, we reviewed state-of-the-art AI in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy and offered a practical guide for building a learning image dataset for algorithm development.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Computer-aided diagnosis; Deep learning; Gastrointestinal endoscopy; Learning dataset.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ruffle JK, Farmer AD, Aziz Q. Artificial intelligence-assisted gastroenterology- promises and pitfalls. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:422–428. - PubMed
-
- Samuel AL. Some studies in machine learning using the game of checkers. IBM J Res Dev. 1959;3:210–229.
-
- Rajkomar A, Dean J, Kohane I. Machine learning in medicine. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1347–1358. - PubMed
-
- McCulloch WS, Pitts W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. 1943. Bull Math Biol. 1990;52:99–115. - PubMed
-
- Litjens G, Ciompi F, Wolterink JM, et al. State-of-the-art deep learning in cardiovascular image analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019;12:1549–1565. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

