Instructing durable humoral immunity for COVID-19 and other vaccinable diseases
- PMID: 35637104
- PMCID: PMC9085459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.05.004
Instructing durable humoral immunity for COVID-19 and other vaccinable diseases
Abstract
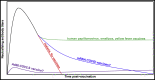
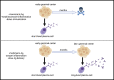
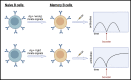
Many aspects of SARS-CoV-2 have fully conformed with the principles established by decades of viral immunology research, ultimately leading to the crowning achievement of highly effective COVID-19 vaccines. Nonetheless, the pandemic has also exposed areas where our fundamental knowledge is thinner. Some key unknowns are the duration of humoral immunity post-primary infection or vaccination and how long booster shots confer protection. As a corollary, if protection does not last as long as desired, what are some ways it can be improved? Here, I discuss lessons from other infections and vaccines that point to several key features that influence durable antibody production and the perseverance of immunity. These include (1) the specific innate sensors that are initially triggered, (2) the kinetics of antigen delivery and persistence, (3) the starting B cell receptor (BCR) avidity and antigen valency, and (4) the memory B cell subsets that are recalled by boosters. I further highlight the fundamental B cell-intrinsic and B cell-extrinsic pathways that, if understood better, would provide a rational framework for vaccines to reliably provide durable immunity.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; durable immunity; plasma cells; vaccines; viruses.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Sana Biotechnology has licensed intellectual property of D.B. and Washington University in St. Louis. Gilead Sciences has licensed intellectual property of D.B. and Stanford University. D.B. is a co-founder of Clade Therapeutics. D.B. serves on an advisory panel for GlaxoSmithKline. D.B. and The University of Arizona hold a patent on SARS-CoV-2 serological assays.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott R.K., Lee J.H., Menis S., Skog P., Rossi M., Ota T., Kulp D.W., Bhullar D., Kalyuzhniy O., Havenar-Daughton C., et al. Precursor frequency and affinity determine B cell competitive fitness in germinal centers, tested with germline-targeting HIV vaccine immunogens. Immunity. 2018;48:133–146.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.11.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alameh M.-G., Tombácz I., Bettini E., Lederer K., Sittplangkoon C., Wilmore J.R., Gaudette B.T., Soliman O.Y., Pine M., Hicks P., et al. Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity. 2021;54:2877–2892.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

