Structural insights into binding of therapeutic channel blockers in NMDA receptors
- PMID: 35637422
- PMCID: PMC10075384
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-022-00772-0
Structural insights into binding of therapeutic channel blockers in NMDA receptors
Abstract
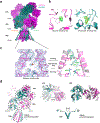
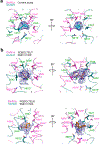
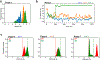
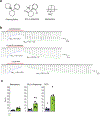
Excitatory signaling mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) is critical for brain development and function, as well as for neurological diseases and disorders. Channel blockers of NMDARs are of medical interest owing to their potential for treating depression, Alzheimer's disease, and epilepsy. However, precise mechanisms underlying binding and channel blockade have remained limited owing to challenges in obtaining high-resolution structures at the binding site within the transmembrane domains. Here, we monitor the binding of three clinically important channel blockers: phencyclidine, ketamine, and memantine in GluN1-2B NMDARs at local resolutions of 2.5-3.5 Å around the binding site using single-particle electron cryo-microscopy, molecular dynamics simulations, and electrophysiology. The channel blockers form different extents of interactions with the pore-lining residues, which control mostly off-speeds but not on-speeds. Our comparative analyses of the three unique NMDAR channel blockers provide a blueprint for developing therapeutic compounds with minimal side effects.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Mayer ML, Westbrook GL & Guthrie PB Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature 309, 261–263 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Mayer ML, MacDermott AB, Westbrook GL, Smith SJ & Barker JL Agonist- and voltage-gated calcium entry in cultured mouse spinal cord neurons under voltage clamp measured using arsenazo III. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 7, 3230–3244 (1987). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

