Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate m6A modification and regulates sepsis-associated acute lung injury by activating ferroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells
- PMID: 35637949
- PMCID: PMC9134924
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.69141
Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate m6A modification and regulates sepsis-associated acute lung injury by activating ferroptosis in alveolar epithelial cells
Abstract
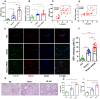
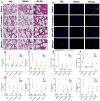
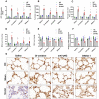
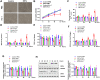
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) production is a major strategy employed by polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) to fight against microbes. NETs have been implicated in the pathogenesis of various lung injuries, although few studies have explored NETs in sepsis-associated acute lung injury (SI-ALI). Here, we demonstrate a major contribution of NETs to the pathology of sepsis-associated ALI by inducing ferroptosis of alveolar epithelial cells. Using both in vitro and in vivo studies, our findings show enhanced NETs accumulation in sepsis-associated ALI patients and mice, as well as the closely related upregulation of ferroptosis, the induction of which depends on METTL3-induced m6A modification of GPX4. Using a CLP-induced sepsis-associated ALI mouse model established with METTL3-/- versus WT mice, in addition to METTL3 knockout and overexpression in vitro, we elucidated and confirmed the critical role of ferroptosis in NETs-induced ALI. These findings support a role for NETs-induced METTL3 modification and the subsequent induction of ferroptosis in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated ALI.
Keywords: N6-Methylation; Neutrophil extracellular traps; ferroptosis; sepsis-associated acute lung injury.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Butt Y, Kurdowska A, Allen TC. Acute Lung Injury: A Clinical and Molecular Review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016 Apr;140(4):345–50. - PubMed
-
- Asaduzzaman M, Lavasani S, Rahman M, Zhang S, Braun OO, Jeppsson B, Thorlacius H. Platelets support pulmonary recruitment of neutrophils in abdominal sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2009 Apr;37(4):1389–96. - PubMed
-
- Memtsoudis SG, Bombardieri AM, Ma Y, Walz JM, Chiu YL, Mazumdar M. Mortality of patients with respiratory insufficiency and adult respiratory distress syndrome after surgery: the obesity paradox. J Intensive Care Med. 2012. Sep-Oct;27(5):306-11. - PubMed
-
- Sweeney RM, Griffiths M, McAuley D. Treatment of acute lung injury: current and emerging pharmacological therapies. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2013 Aug;34(4):487–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

