Ilixadencel, a Cell-based Immune Primer, plus Sunitinib Versus Sunitinib Alone in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Randomized Phase 2 Study
- PMID: 35638086
- PMCID: PMC9142735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euros.2022.03.012
Ilixadencel, a Cell-based Immune Primer, plus Sunitinib Versus Sunitinib Alone in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Randomized Phase 2 Study
Abstract
Background: The prognosis of patients with synchronous metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) is poor. Whereas single-agent tyrosine kinase inhibition (TKI) is clearly insufficient, the effects can be enhanced by combinations with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Innovative treatment options combining TKI and other immune-stimulating agents could prove beneficial.
Objective: To evaluate the clinical effects on metastatic disease when two doses of allogeneic monocyte-derived dendritic cells (ilixadencel) are administrated intratumorally followed by nephrectomy and treatment with sunitinib compared with nephrectomy and sunitinib monotherapy, in patients with synchronous mRCC.
Design setting and participants: A randomized (2:1) phase 2 multicenter trial enrolled 88 patients with newly diagnosed mRCC to treatment with the combination ilixadencel/sunitinib (ILIXA/SUN; 58 patients) or sunitinib alone (SUN; 30 patients).
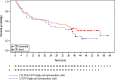
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: The primary endpoints were 18-mo survival rate and overall survival (OS). A secondary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) assessed up to 18 mo after enrollment. Statistic evaluations included Kaplan-Meier estimates, log-rank tests, Cox regression, and stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel tests.
Results and limitations: The median OS was 35.6 mo in the ILIXA/SUN arm versus 25.3 mo in the SUN arm (hazard ratio 0.73, 95% confidence interval 0.42-1.27; p = 0.25), while the 18-mo OS rates were 63% and 66% in the ILIXA/SUN and SUN arms, respectively. The confirmed ORR in the ILIXA/SUN arm were 42.2% (19/45), including three patients with complete response, versus 24.0% (six/25) in the SUN arm (p = 0.13) without complete responses. The study was not adequately powered to detect modest differences in survival.
Conclusions: The study failed to meet its primary endpoints. However, ilixadencel in combination with sunitinib was associated with a numerically higher, nonsignificant, confirmed response rate, including complete responses, compared with sunitinib monotherapy.
Patient summary: We studied the effects of intratumoral vaccination with ilixadencel followed by sunitinib versus sunitinib only in a randomized phase 2 study. The combination treatment showed numerically higher numbers of confirmed responses, suggesting an immunologic effect.
Keywords: Allogeneic dendritic cells; Ilixadencel; Intratumoral administration; Metastatic renal cell carcinoma; Off the shelf; Phase 2 trial; Randomized; Sunitinib.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Capitanio U., Montorsi F. Renal cancer. Lancet. 2016;387:894–906. - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg B., Campbell S.C., Choi H.Y., et al. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2011;60:615–621. - PubMed
-
- Powles T., Staehler M., Ljungberg B., et al. European Association of Urology guidelines for clear cell renal cancers that are resistant to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted therapy. Eur Urol. 2016;70:705–706. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

