ARHGEF9 gene variant leads to developmental and epileptic encephalopathy: Genotypic phenotype analysis and treatment exploration
- PMID: 35638461
- PMCID: PMC9266599
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.1967
ARHGEF9 gene variant leads to developmental and epileptic encephalopathy: Genotypic phenotype analysis and treatment exploration
Abstract
Background: The ARHGEF9 gene variants have phenotypic heterogeneity, the number of reported clinical cases are limited and the genotype-phenotype relationship is still unpredictable.
Methods: Clinical data of the patients and their family members were gathered in a retrospective study. The exome sequencing that was performed on peripheral blood samples was applied for genetic analysis. We used the ARHGEF9 gene as a key word to search the PubMed database for cases of ARHGEF9 gene variants that have previously been reported and summarized the reported ARHGEF9 gene variant sites, their corresponding clinical phenotypes, and effective treatment.
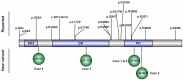
Results: We described five patients with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy caused by ARHGEF9 gene variants. Among them, the antiepileptic treatment of valproic acid and levetiracetam was effective in two cases individually. The exome sequencing results showed five children with point mutations in the ARHGEF9 gene: p.R365H, p.M388V, p.D213E, and p.R63H. So far, a total of 40 children with ARHGEF9 gene variants have been reported. Their main clinical phenotypes include developmental delay, epilepsy, epileptic encephalopathy, and autism spectrum disorders. The variants reported in the literature, including 22 de novo variants, nine maternal variants, and one unknown variant. There were 20 variants associated with epileptic phenotypes, of which six variants are effective for valproic acid treatment.
Conclusion: The genotypes and phenotypes of ARHGEF9 gene variants represent a wide spectrum, and the clinical phenotype of epilepsy is often refractory and the prognosis is poor. The p.R365H, p.M388V, p.D213E, and p.R63H variants have not been reported in the current literature, and our study has expanded the genotype spectrum of ARHGEF9 gene. Our findings indicate that levetiracetam and valproic acid can effectively control seizures in children with epileptic phenotype caused by ARGHEF9 gene variations. These findings will help clinicians improve the level of diagnosis and treatment of the genetic disease.
Keywords: ARHGEF9 gene; child; developmental delay; epilepsy; treatment.
© 2022 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aarabi, M. , Kessler, E. , Madan‐Khetarpal, S. , Surti, U. , Bellissimo, D. , Rajkovic, A. , & Yatsenko, S. A. (2019). Autism spectrum disorder in females with ARHGEF9 alterations and a random pattern of X chromosome inactivation. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 62(4), 239–242. - PubMed
-
- Alber, M. , Kalscheuer, V. M. , Marco, E. , Sherr, E. , Lesca, G. , Till, M. , Gradek, G. , Wiesener, A. , Korenke, C. , Mercier, S. , Becker, F. , Yamamoto, T. , Scherer, S. W. , Marshall, C. R. , Walker, S. , Dutta, U. R. , Dalal, A. B. , Suckow, V. , Jamali, P. , … Minassian, B. A. (2017). ARHGEF9 disease: Phenotype clarification and genotype‐phenotype correlation. Neurology Genetics, 3(3), e148. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhat, G. , LaGrave, D. , Millson, A. , Herriges, J. , Lamb, A. N. , & Matalon, R. (2016). Xq11.1‐11.2 deletion involving ARHGEF9 in a girl with autism spectrum disorder. European Journal of Medical Genetics, 59(9), 470–473. - PubMed
-
- Freri, E. , Castellotti, B. , Didato, G. , DiFrancesco, J. C. , & Granata, T. (2020). Epilepsy and NREM‐parasomnia caused by novel hemizygous ARHGEF9 mutation. Sleep Medicine, 76, 158–159. - PubMed
-
- Harvey, K. , Duguid, I. C. , Alldred, M. J. , Beatty, S. E. , Ward, H. , Keep, N. H. , Lingenfelter, S. E. , Pearce, B. R. , Lundgren, J. , Owen, M. J. , Smart, T. G. , Lüscher, B. , Rees, M. I. , & Harvey, R. J. (2004). The GDP‐GTP exchange factor collybistin: an essential determinant of neuronal gephyrin clustering. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24(25), 5816–5826. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases