MRI-based Texture Analysis of Infrapatellar Fat Pad to Predict Knee Osteoarthritis Incidence
- PMID: 35638929
- PMCID: PMC9434820
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.212009
MRI-based Texture Analysis of Infrapatellar Fat Pad to Predict Knee Osteoarthritis Incidence
Abstract
Background Infrapatellar fat pad (IPFP) quality has been implicated as a marker for predicting knee osteoarthritis (KOA); however, no valid quantification for subtle IPFP abnormalities has been established. Purpose To investigate whether MRI-based three-dimensional texture analysis of IPFP abnormalities could help predict incident radiographic KOA. Materials and Methods In this prospective nested case-control study, 690 participants whose knees were at risk for KOA were included from the Pivotal Osteoarthritis Initiative MRI Analyses incident osteoarthritis cohort. All knees had a Kellgren-Lawrence grade of 1 or less at baseline. During the 4-year follow-up, case participants were matched 1:1 to control participants, with incident radiographic KOA as the outcome. MRI scans were segmented at the incident time point of KOA (hereafter, P0), 1 year before P0 (hereafter, P-1), and baseline. MRI-based three-dimensional texture analysis was performed to extract IPFP texture features. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and multivariable logistic regressions were applied in the development cohort and evaluated in the test cohort. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was used to evaluate the discriminative value of the clinical score, IPFP texture score, and MRI Osteoarthritis Knee Score. Results Participants were allocated to development (n = 500, 340 women; mean age, 60 years) and test (n = 190, 120 women; mean age, 61 years) cohorts. In both cohorts, IPFP texture scores (AUC ≥0.75 for all) showed greater discrimination than clinical scores (AUC ≤0.69 for all) at baseline, P-1, and P0, with significant differences in pairwise comparisons (P ≤ .002 for all). Greater predictive and concurrent validities of IPFP texture scores (AUC ≥0.75 for all) compared with MRI Osteoarthritis Knee Scores (AUC ≤0.66 for all) were also demonstrated (P < .001 for all). Conclusion MRI-based three-dimensional texture of the infrapatellar fat pad was associated with future development of knee osteoarthritis. ClinicalTrials.gov registration no.: NCT00080171 © RSNA, 2022 Online supplemental material is available for this article. See also the editorial by Fischer in this issue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

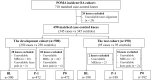

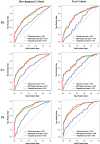
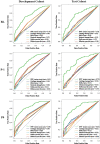
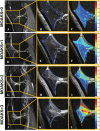
Comment in
-
From Morphology to Biomarker: Quantitative Texture Analysis of the Infrapatellar Fat Pad Reliably Predicts Knee Osteoarthritis.Radiology. 2022 Sep;304(3):622-623. doi: 10.1148/radiol.221094. Epub 2022 May 31. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 35638934 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hunter DJ , Bierma-Zeinstra S . Osteoarthritis . Lancet 2019. ; 393 ( 10182 ): 1745 – 1759 . - PubMed
-
- Sharma L . Osteoarthritis of the Knee . N Engl J Med 2021. ; 384 ( 1 ): 51 – 59 . - PubMed
-
- Zhu Z , Li J , Ruan G , Wang G , Huang C , Ding C . Investigational drugs for the treatment of osteoarthritis, an update on recent developments . Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2018. ; 27 ( 11 ): 881 – 900 . - PubMed
-
- Li J , Zhu Z , Li Y , et al. . Qualitative and quantitative measures of prefemoral and quadriceps fat pads are associated with incident radiographic osteoarthritis: data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative . Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2020. ; 28 ( 4 ): 453 – 461 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

