Trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with central nervous system involvement from HER2-positive breast cancer: The DEBBRAH trial
- PMID: 35639825
- PMCID: PMC9825345
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/noac144
Trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with central nervous system involvement from HER2-positive breast cancer: The DEBBRAH trial
Abstract
Background: Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) has shown durable antitumor activity in pretreated patients with HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (ABC), but its efficacy has not yet been evaluated in patients with active brain metastases (BMs). DEBBRAH aims to assess T-DXd in patients with HER2-positive or HER2-low ABC and central nervous system involvement.
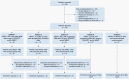
Methods: This ongoing, five-cohort, phase II study (NCT04420598) enrolled patients with pretreated HER2-positive or HER2-low ABC with stable, untreated, or progressing BMs, and/or leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Here, we report findings from HER2-positive ABC patients with non-progressing BMs after local therapy (n = 8; cohort 1), asymptomatic untreated BMs (n = 4; cohort 2), or progressing BMs after local therapy (n = 9; cohort 3). Patients received 5.4 mg/kg T-DXd intravenously once every 21 days. The primary endpoint was 16-week progression-free survival (PFS) for cohort 1 and intracranial objective response rate (ORR-IC) for cohorts 2 and 3.
Results: As of October 20, 2021, 21 patients received T-DXd. In cohort 1, 16-week PFS rate was 87.5% (95%CI, 47.3-99.7; P < .001). ORR-IC was 50.0% (95%CI, 6.7-93.2) in cohort 2 and 44.4% (95%CI, 13.7-78.8; P < .001) in cohort 3. Overall, the ORR-IC in patients with active BMs was 46.2% (95%CI, 19.2-74.9). Among patients with measurable intracranial or extracranial lesions at baseline, the ORR was 66.7% (12 out of 18 patients; 95%CI, 41.0-86.7), 80.0% (95%CI, 28.4-99.5) in cohort 1, 50.0% (95%CI, 6.7-93.2) in cohort 2, and 66.7% (95%CI, 29.9-92.5) in cohort 3. All responders had partial responses. The most common adverse events included fatigue (52.4%; 4.8% grade ≥3), nausea (42.9%; 0% grade ≥3), neutropenia (28.6%; 19% grade ≥3), and constipation (28.6%; 0% grade ≥3). Two (9.5%) patients suffered grade 1 interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis.
Conclusions: T-DXd showed intracranial activity with manageable toxicity and maintained the quality of life in pretreated HER2-positive ABC patients with stable, untreated, or progressing BMs. Further studies are needed to validate these results in larger cohorts.
Keywords: HER2-positive; T-DXd; advanced breast cancer; brain metastases; trastuzumab deruxtecan.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology.
Figures

References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines: Central Nervous System Cancers v2.2021. Plymouth Meeting, PA: National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN); 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

