A novel high-throughput single B-cell cloning platform for isolation and characterization of high-affinity and potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 35640847
- PMCID: PMC9142369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105349
A novel high-throughput single B-cell cloning platform for isolation and characterization of high-affinity and potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies
Abstract
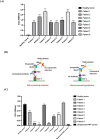
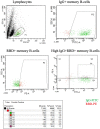
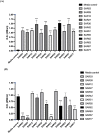
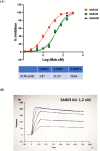
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that are specific to SARS-CoV-2 can be useful in diagnosing, preventing, and treating the coronavirus (COVID-19) illness. Strategies for the high-throughput and rapid isolation of these potent neutralizing antibodies are critical toward the development of therapeutically targeting COVID-19 as well as other infectious diseases. In the present study, a single B-cell cloning method was used to screen the Wuhan-Hu-1 strain of SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) specific, high affinity, and neutralizing mAbs from patients' blood samples. An RBD-specific antibody, SAR03, was discovered that showed high binding (ELISA and SPR) and neutralizing activity (competitive ELISA and pseudovirus-based reporter assay) against the Wuhan-Hu-1 strain of SARS-CoV-2. Mechanistic studies on human cells revealed that SAR03 competes with the ACE-2 receptor for binding with the RBD domain (S1 subunit) present in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. This study highlights the potential of the single B cell cloning method for the rapid and efficient screening of high-affinity and effective neutralizing antibodies for SARS-CoV-2 and other emerging infectious diseases.
Keywords: ELISA; RBD domain; SARS-CoV-2; SPR; Single B-cell cloning; mAbs.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chi X., Yan R., Zhang J., Zhang G., Zhang Y., Hao M., Zhang Z., Fan P., Dong Y., Yang Y., Chen Z., Guo Y., Zhang J., Li Y., Song X., Chen Y., Xia L., Fu L., Hou L., Xu J., Yu C., Li J., Zhou Q., Chen W. A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science. 2020;369:650–655. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Han X., Wang Y., Li S., Hu C., Li T., Gu C., Wang K., Shen M., Wang J., Hu J., Wu R., Mu S., Gong F., Chen Q., Gao F., Huang J., Long Y., Luo F., Song S., Long S., Hao Y., Li L., Wu Y., Xu W., Cai X., Gao Q., Zhang G., He C., Deng K., Du L., Nai Y., Wang W., Xie Y., Qu D., Huang A., Tang N., Jin A. A rapid and efficient screening system for neutralizing antibodies and its application for SARS-CoV-2. Front. Immunol. 2021;12 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kohler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975;256:495–497. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

