Serum O-glycosylated hepatitis B surface antigen levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B during nucleos(t)ide analog therapy
- PMID: 35641912
- PMCID: PMC9153111
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02352-4
Serum O-glycosylated hepatitis B surface antigen levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B during nucleos(t)ide analog therapy
Abstract
Background: Serum hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is a component of both hepatitis B virus (HBV) virions and non-infectious subviral particles (SVPs). Recently, O-glycosylation of the PreS2 domain of middle HBsAg protein has been identified as a distinct characteristic of genotype C HBV virions versus SVPs. This study aimed to evaluate serum O-glycosylated HBsAg levels in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs (NAs).
Methods: Forty-seven treatment-naïve patients with genotype C CHB were retrospectively enrolled. Serum O-glycosylated HBsAg levels at baseline and after 48 weeks of NA therapy were quantified by immunoassay using a monoclonal antibody against the O-glycosylated PreS2 domain of middle HBsAg, and their correlations with conventional HBV marker levels were analyzed.
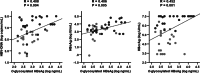
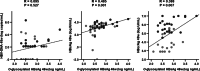
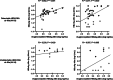
Results: At baseline, the serum O-glycosylated HBsAg levels were significantly correlated with the HBV DNA (P = 0.004), HBsAg (P = 0.005), and hepatitis B-core related antigen (HBcrAg, P = 0.001) levels. Both HBV DNA and O-glycosylated HBsAg levels were decreased after 48 weeks of NA therapy. The significant correlation of the O-glycosylated HBsAg level with the HBsAg or HBcrAg level was lost in patients who achieved undetectable HBV DNA (HBsAg, P = 0.429; HBcrAg, P = 0.065). Immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that HBV DNA and RNA were detected in the O-glycosylated HBsAg-binding serum fraction, and the proportion of HBV RNA increased during NA therapy (P = 0.048).
Conclusion: Serum O-glycosylated HBsAg levels change during NA therapy and may reflect combined levels of serum HBV DNA and RNA virions. An O-glycosylated HBsAg-based immunoassay may provide a novel means to monitor viral kinetics during NA therapy.
Keywords: Hepatitis B surface antigen; Hepatitis B virus; O-Glycan; Pregenomic RNA; Virion.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TG has received honoraria from AbbVie, Gilead Sciences Inc., and MSD K.K., and research funding from AbbVie, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, JIMRO, and Takeda Pharmaceutical. KA, MS, and HN are employees and CEO of RCMG, Inc., one of the AIST venture companies. AM, SS, and TI had no competing interests.
Figures

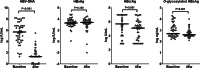

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

