The two-faced role of ATF2 on cisplatin response in gastric cancer depends on p53 context
- PMID: 35641966
- PMCID: PMC9153165
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-022-00802-w
The two-faced role of ATF2 on cisplatin response in gastric cancer depends on p53 context
Abstract
Background: Activating transcription factor-2 (ATF2) is a member of the basic leucine zipper family of DNA-binding proteins, which exhibits both oncogenic and tumor suppression activity in different tumors. However, the molecular mechanism of its dual function in cancer chemotherapy especially in gastric cancer has still not been elucidated.
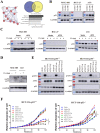
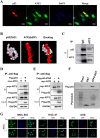
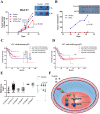
Methods: The protein expression and location of ATF2 in gastric cancer tissues was detected with immunohistochemistry assay, and the clinical significance was analyzed using TCGA and GEO database. The activation and impact of ATF2 in cisplatin treated cells were evaluated with western blot, incucyte live cell analysis, clone formation and tumor xenografts assays. Interaction between ATF2 and p53 was confirmed with immunoprecipitation and GST-pull down. Potential molecular mechanism of ATF2 in different p53 status cells was analyzed with RNA sequencing and real-time quantitative PCR.
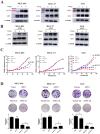
Results: ATF2 mainly located in the nucleus of cancer cells, higher ATF2 level was associated with poor five-year survival of gastric patients, especially in those undergone chemotherapy treatment. Cisplatin treatment significantly activated ATF2 in p53 mutant cells. ATF2 could interact with the trans-activation domain of p53 and enhance cisplatin sensitivity in p53 wild type cell lines, while promoted cell survival in mutant p53 cancer cells by affecting ERK1/2 pathway.
Conclusions: This study confirmed the effect of ATF2 on cisplatin sensitivity was associated with the functional status of p53 in gastric cancer cells. Integrated analysis of ATF2 expression and P53 status could be used to evaluate the chemotherapy sensitivity and prognosis of gastric cancer patients.
Keywords: ATF2; Cisplatin; ERK1/2; Gastric cancer; Prognosis; p53.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) by DNA-damaging agents serves to promote drug resistance via activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2)-dependent enhanced DNA repair.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 6;278(23):20582-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210992200. Epub 2003 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12663670
-
ATF2 contributes to cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer and celastrol induces cisplatin resensitization through inhibition of JNK/ATF2 pathway.Int J Cancer. 2015 Jun 1;136(11):2598-609. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29302. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25359574
-
Association of activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme hUBC9. Implication of the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway in regulation of ATF2 in T cells.J Biol Chem. 1998 Mar 6;273(10):5892-902. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.10.5892. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9488727
-
Emerging roles of activating transcription factor 2 in the development of breast cancer: a comprehensive review.Precis Clin Med. 2023 Oct 25;6(4):pbad028. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbad028. eCollection 2023 Dec. Precis Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37955015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The activating transcription factor 2: an influencer of cancer progression.Mutagenesis. 2019 Dec 19;34(5-6):375-389. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gez041. Mutagenesis. 2019. PMID: 31799611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

