Nalbuphine alleviates inflammation by down-regulating NF-κB in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model
- PMID: 35642022
- PMCID: PMC9158276
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-022-00573-7
Nalbuphine alleviates inflammation by down-regulating NF-κB in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model
Abstract
Introduction: Nalbuphine can relieve patients' inflammation response after surgery compared to other opioid drugs. However, its molecular mechanism has not been clear. Activation of NF-κB signaling pathway under oxidative stress and inflammation can maintain pain escalation.
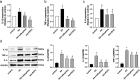
Methods: We firstly investigated the effect of nalbuphine on writhing test and mechanical allodynia using a rat model of inflammatory visceral pain (acetic acid (AA) administrated). Cytokines (including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, Interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-2, and IL-6 in plasma were tested with ELISA technology. Expression levels of TNF-α, IκBα and p-NF-κB p65 at the spinal cord (L3-5) were measured by western blot or RT-qPCR.
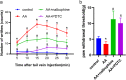
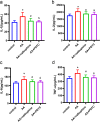
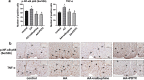
Results: We found that the paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) values of rats were reduced in the model group, while the numbers of writhing, levels of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α in plasma, and p-NF-κB protein and its gene expressions in the lumbar spinal cord were up-regulated. Subcutaneously injection of nalbuphine (10 μg/kg) or PDTC (NF-κB inhibitor) attenuated acetic acid-induced inflammatory pain, and this was associated with reversal of up-regulated IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α in both plasma and spinal cord. Furthermore, acetic acid increased p-NF-κB and TNF-α protein levels in the white matter of the spinal cord, which was attenuated by nalbuphine. These results suggested that nalbuphine can significantly ameliorate inflammatory pain via modulating the expression of NF-κB p65 as well as inflammation factors level in the spinal cord.
Conclusion: In conclusion, nalbuphine inhibits inflammation through down-regulating NF-κB pathway at the spinal cord in a rat model of inflammatory visceral pain.
Keywords: Inflammation; NF-κB; Nalbuphine; Visceral pain.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
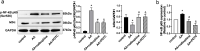
Similar articles
-
[Moxibustion relieves colonic inflammation by up-regulating expression of miR-345-3p/miR-216a-5p and down-regulating NF-κB p65 in colonic tissue of rats with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Mar 25;48(3):226-32. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20220005. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 36951073 Chinese.
-
Analgesic effect of resveratrol on colitis-induced visceral pain via inhibition of TRAF6/NF-κB signaling pathway in the spinal cord.Brain Res. 2019 Dec 1;1724:146464. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2019.146464. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 31536729
-
Nrf2 mediates the antinociceptive activity of dexmedetomidine in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model by activating the NF-κB sensor.Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Jan;38(1):97-105. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3456. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. PMID: 31773760
-
Resolvin D1 Inhibits Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Sciatica by Modulating the Expression of Nuclear Factor-κB, Phospho-extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase, and Pro- and Antiinflammatory Cytokines in the Spinal Cord and Dorsal Root Ganglion.Anesthesiology. 2016 Apr;124(4):934-44. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001010. Anesthesiology. 2016. PMID: 26808633
-
Trifluoro-icaritin alleviates chronic inflammatory pain through α7nAChR-mediated suppression of HMGB1/NF-κB signaling in the spinal cord of rats.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Jun 1;183:13-26. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.02.014. Epub 2022 Feb 22. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 35202753
Cited by
-
Analgesic Effect of Dexmedetomidine-Nalbuphine Combination vs. Dexmedetomidine Alone in Donkeys Undergoing Field Castration under Total Intravenous Anesthesia.Animals (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;14(17):2452. doi: 10.3390/ani14172452. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272237 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of nalbuphine and dezocine for postoperative analgesia in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic radical gastric cancer surgery.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):8073-8082. doi: 10.62347/NJIA6803. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39822490 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study and subsequent functional analysis reveal regulatory mechanism underlying piglet diarrhea.Anim Biosci. 2025 Apr;38(4):612-628. doi: 10.5713/ab.24.0547. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Anim Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39482997 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperlipidemia Increases Nalbuphine Brain Accumulation with Multiple Dosing without Affecting Its Analgesic Response-Its Respiratory Depression Potential Should Be Investigated in Future Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 22;17(3):282. doi: 10.3390/ph17030282. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543067 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

