Foxf1 gene increases the risk of osteoporosis in rats by inhibiting osteoblast formation and promoting osteoclast differentiation through the upregulation of NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 35642703
- PMCID: PMC9186464
Foxf1 gene increases the risk of osteoporosis in rats by inhibiting osteoblast formation and promoting osteoclast differentiation through the upregulation of NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Objectives: a) To explore the expression of Foxf1 and NF-κB in bone tissue of ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis and b) to investigate the role and mechanism of NF-κB pathway regulated by Foxf1 gene in the differentiation and formation of rat osteoclasts and osteoblasts with cell experiments.
Methods: Ovariectomized rat model of osteoporosis was established with 3-month-old female SD rats. The rats were divided into sham group (n=10) and osteoporosis group (n=10). Real time fluorescent quantitative PCR and Western blot were used to detect the expression levels of Foxf1 and NF-κB genes and proteins in the femur tissues of rats and analyze their correlation.
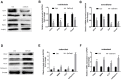
Results: Both Foxf1 and NF- κB were highly expressed in the femur tissues. Upon the overexpression of Foxf1 gene in osteoblasts and osteoclasts in vitro, the gene and protein expression of NF-κB were also upregulated, significantly reducing the gene and protein expression levels of osteogenic factors, including ATF4, OCN, ALP and Runx2.
Conclusions: Foxf1 gene could inhibit osteoblast formation and promote osteoclast differentiation by NF-κB pathway, which may increase the risk of osteoporosis in rats.
Keywords: Foxf1 Gene; NF-κB Pathway; Osteoblasts; Osteoclasts; Osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
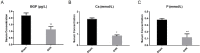


References
-
- Compston JE, McClung MR, Leslie WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393:364–376. - PubMed
-
- Porter JL, Varacallo M. Osteoporosis. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL):StatPearls Publishing Copyright ©2020, StatPearls Publishing LLC, 2020
-
- van Staa TP, Dennison EM, Leufkens HG, Cooper C. Epidemiology of fractures in England and Wales. Bone. 2001;29:517–522. - PubMed
-
- Eastell R, O'Neill TW, Hofbauer LC, Langdahl B, Reid IR, Gold DT, Cummings SR. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16069. - PubMed
