TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and C-reactive protein in predicting the progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 35643306
- PMCID: PMC9132472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.05.051
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, interferon gamma-induced protein 10, and C-reactive protein in predicting the progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Early prognostication of COVID-19 severity will potentially improve patient care. Biomarkers, such as TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), interferon gamma-induced protein 10 (IP-10), and C-reactive protein (CRP), might represent possible tools for point-of-care testing and severity prediction.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, we analyzed serum levels of TRAIL, IP-10, and CRP in patients with COVID-19, compared them with control subjects, and investigated the association with disease severity.
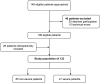
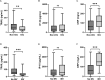
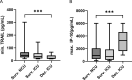
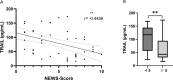
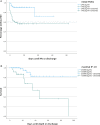
Results: A total of 899 measurements were performed in 132 patients (mean age 64 years, 40.2% females). Among patients with COVID-19, TRAIL levels were lower (49.5 vs 87 pg/ml, P = 0.0142), whereas IP-10 and CRP showed higher levels (667.5 vs 127 pg/ml, P <0.001; 75.3 vs 1.6 mg/l, P <0.001) than healthy controls. TRAIL yielded an inverse correlation with length of hospital and intensive care unit (ICU) stay, Simplified Acute Physiology Score II, and National Early Warning Score, and IP-10 showed a positive correlation with disease severity. Multivariable regression revealed that obesity (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 5.434, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.005-29.38), CRP (aOR 1.014, 95% CI 1.002-1.027), and peak IP-10 (aOR 1.001, 95% CI 1.00-1.002) were independent predictors of in-ICU mortality.
Conclusions: We demonstrated a correlation between COVID-19 severity and TRAIL, IP-10, and CRP. Multivariable regression showed a role for IP-10 in predicting unfavourable outcomes, such as in-ICU mortality.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, NCT04655521.
Keywords: Biomarkers; COVID-19; CRP; Host response; IP-10; Point-of-care testing; Severity prediction; TRAIL.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Arnold DT, Attwood M, Barratt S, Morley A, Elvers KT, McKernon J, et al. Predicting outcomes of COVID-19 from admission biomarkers: a prospective UK cohort study. Emerg Med J. 2021;38:543–548. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

