Engineering a carbohydrate-binding module to increase the expression level of glucoamylase in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 35643500
- PMCID: PMC9148494
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-022-01833-1
Engineering a carbohydrate-binding module to increase the expression level of glucoamylase in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
Background: Glucoamylase is an important industrial enzyme for the saccharification of starch during sugar production, but the production cost of glucoamylase is a major limiting factor for the growth of the starch-based sugar market. Therefore, seeking strategies for high-level expression of glucoamylase in heterologous hosts are considered as the main way to reduce the enzyme cost.
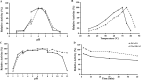
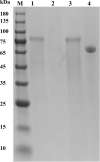
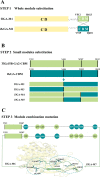
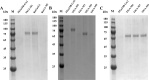
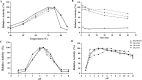
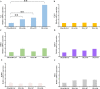
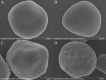
Results: ReGa15A from Rasamsonia emersonii and TlGa15B-GA2 from Talaromyces leycettanus have similar properties. However, the secretion level of ReGa15A was significantly higher than TlGa15B-GA2 in Pichia pastoris. To explore the underlying mechanisms affecting the differential expression levels of glucoamylase in P. pastoris, the amino acid sequences and three-dimensional structures of them were compared and analyzed. First, the CBM region was identified by fragment replacement as the key region affecting the expression levels of ReGa15A and TlGa15B-GA2. Then, through the substitution and site-directed mutation of the motifs in the CBM region, three mutants with significantly increased expression levels were obtained. The eight-point mutant TlGA-M4 (S589D/Q599A/G600Y/V603Q/T607I/V608L/N609D/R613Q), the three-point mutant TlGA-M6 (Q599A/G600Y/V603Q) and the five-point mutant TlGA-M7 (S589D/T607I/V608L/N609D/R613Q) have the same specific activity with the wild-type, and the enzyme activity and secretion level have increased by 4-5 times, respectively. At the same time, the expression levels were 5.8-, 2.0- and 2.4-fold higher than that of wild type, respectively. Meanwhile, the expression of genes related to the unfolded protein responses (UPR) in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) did not differ significantly between the mutants and wild type. In addition, the most highly expressed mutant, TlGA-M7 exhibits rapidly and effectively hydrolyze raw corn starch.
Conclusions: Our results constitute the first demonstration of improved expression and secretion of a glucoamylase in P. pastoris by introducing mutations within the non-catalytic CBM. This provides a novel and effective strategy for improving the expression of recombinant proteins in heterologous host expression systems.
Keywords: Carbohydrate-binding module; Glucoamylase; Pichia pastoris; Protein expression level; Site-directed mutagenesis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

