Cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in children under five years of age in 195 countries: A meta-regression analysis
- PMID: 35643565
- PMCID: PMC9208428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.05.042
Cost-effectiveness of rotavirus vaccination in children under five years of age in 195 countries: A meta-regression analysis
Abstract
Background: Rotavirus caused an estimated 151,714 deaths from diarrhea among children under 5 in 2019. To reduce mortality, countries are considering adding rotavirus vaccination to their routine immunization program. Cost-effectiveness analyses (CEAs) to inform these decisions are not available in every setting, and where they are, results are sensitive to modeling assumptions, especially about vaccine efficacy. We used advances in meta-regression methods and estimates of vaccine efficacy by location to estimate incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) for rotavirus vaccination in 195 countries.
Methods: Beginning with Tufts University CEA and Global Health CEA registries we used 515 ICERs from 68 articles published through 2017, extracted 938 additional one-way sensitivity analyses, and excluded 33 ICERs for a sample of 1,418. We used a five-stage, mixed-effects, Bayesian metaregression framework to predict ICERs, and logistic regression model to predict the probability that the vaccine was cost-saving. For both models, covariates were vaccine characteristics including efficacy, study methods, and country-specific rotavirus disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) and gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. All results are reported in 2017 United States dollars.
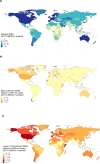
Results: Vaccine efficacy, vaccine cost, GDP per capita and rotavirus DALYs were important drivers of variability in ICERs. Globally, the median ICER was $2,289 (95% uncertainty interval (UI): $147-$38,993) and ranged from $85 per DALY averted (95% UI: $13-$302) in Central African Republic to $70,599 per DALY averted (95% UI: $11,030-$263,858) in the United States. Among countries eligible for support from Gavi, The Vaccine Alliance, the mean ICER was $255 per DALY averted (95% UI: $39-$918), and among countries eligible for the PAHO revolving fund, the mean ICER was $2,464 per DALY averted (95% UI: $382-$3,118).
Conclusion: Our findings incorporate recent evidence that vaccine efficacy differs across locations, and support expansion of rotavirus vaccination programs, particularly in countries eligible for support from Gavi, The Vaccine Alliance.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness analysis; Meta-regression; Rotavirus vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance. Rotavirus vaccine support n.d. https://www.gavi.org/types-support/vaccine-support/rotavirus (accessed November 7, 2021).
-
- ROTA Council. Global Introduction Status. Rota Council n.d. http://preventrotavirus.org/vaccine-introduction/global-introduction-sta... (accessed November 7, 2021).
-
- Thiboonboon K., Santatiwongchai B., Chantarastapornchit V., Rattanavipapong W., Teerawattananon Y. A Systematic Review of Economic Evaluation Methodologies Between Resource-Limited and Resource-Rich Countries: A Case of Rotavirus Vaccines. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2016;14:659–672. doi: 10.1007/s40258-016-0265-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

