The association of family history of herpes zoster and the risk of incident herpes zoster: the SHEZ Study
- PMID: 35644539
- PMCID: PMC9251617
- DOI: 10.1265/ehpm.21-00020
The association of family history of herpes zoster and the risk of incident herpes zoster: the SHEZ Study
Abstract
Background: We investigated whether family histories of herpes zoster (HZ) are associated with the risk of incident HZ in a Japanese population.
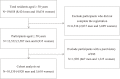
Methods: A total of 12,522 Japanese residents aged ≥50 years in Shozu County participated in the baseline survey between December 2008 and November 2009 (the participation rate = 72.3%). They were interviewed at baseline by research physicians regarding the registrants' history of HZ. A self-administered questionnaire survey was conducted to evaluate the potential confounding factors. 10,530 participants without a history of HZ were followed up to ascertain the incidence of HZ during 3-years follow-up until the end of November 2012 with Japanese nationals. We estimated hazard ratios (HRs) of incident HZ according to first-degree family histories using the Cox proportional hazard regression after adjusting for age, sex, and other potential confounding factors.
Results: Compared to no HZ history of each family member, a history of brother or sister was associated with a higher risk of incident HZ while histories of father and mother were not. The multivariable HR (95%CI) of incident HZ for a history of brother or sister was 1.67 (1.04-2.69). When comparing to no family histories of all first-degree relatives, the multivariable HRs (95%CIs) were 1.34 (0.77-2.34) for a history of brother or sister alone, but 4.81 (1.78-13.00) for a history of mother plus brother or sister. As for the number of family histories, the multivariable HRs (95%CIs) were 1.08 (0.76-1.54) for one relative (father, mother, or brother or sister) and 2.75 (1.13-6.70) for two or more relatives.
Conclusion: Family histories of mother plus brother or sister and two or more first-degree relatives were associated with a higher risk of incident HZ.
Keywords: Family history; Herpes zoster; History of HZ; Incidence; Prospective cohort study.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Opstelten W, Mauritz WJ, de Wit NJ, van Wijck AJM, Stalman ABW, et al.. Herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia: incidence and risk factor using a general practice research database. Fam Pract. 2002;19:471–5. - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Patient Survey 2017. Accessed 3 Mar 2022. http://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/kanja/10syoubyo/index.html.
-
- Schmader K. Herpes zoster in older adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1481–6. - PubMed
-
- Hicks DL, Cook-Norris HR, Mendoza N, Madkan V, Arora A, Tyring KS. Family history as a risk factor for herpes zoster: a case–control study. Arch Dermatol. 2008;114:603–8. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez OP, Javed S, Mendoza N, Lapolla W, Hicks DL, Tyring KS, et al.. Family history and herpes zoster risk in the era of shingles vaccination. J Clin Virol. 2011;52:344–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials